Proper study guides for 1Z0-821 Oracle Solaris 11 System Administrator certified begins with preparation products which designed to deliver the by making you pass the 1Z0-821 test at your first time. Try the free right now.
Check 1Z0-821 free dumps before getting the full version:
NEW QUESTION 1
You created an IP address for interface not.3 with the following command, which executed successfully:
ipadm create-addr –T static –a 192.168.0.100/24 net3/v4
You then ran: ipadm show–if
The result indicated that the interface was down.
You then ran:
ipadm delete-addr net3/v4
ipadm create-addr –T static –a 192.168.0.101/24 net3/v4 ipadm show-if
The last command indicated that the interface was up.
Why did it work with the second address specified, but not the first?
- A. The 192.168.0.100 address is reserved for broadcast messages.
- B. Another device exists on the network, using the 192.168.0.100 address.
- C. The network interface card does not support the address 192.168.0.100.
- D. The address 192.168.0.100 is at a boundary and may not be configured in Oracle Solaris 11.
- E. 192.168.0.100 is a DHCP address and may not be statically configured in Oracle Solaris 11.
Answer: B
Explanation: The first IP address is already in use.
NEW QUESTION 2
The storage pool configuration on your server is:
You back up the /pool1/data file system, creating a snapshot and copying that snapshot to tape (/dev/rmt/0). You perform a full backup on Sunday night and Incremental backups on Monday through Saturday night at 11:00 pm. Each incremental backup will copy only the data that has been modified since the Sunday backup was started.
On Thursday, at 10:00 am, you had a disk failure. You replaced the disk drive (c4t0d0). You created pool (pool1) on that disk.
Which option would you select to restore the data in the /pool1/data file system?
- A. zfs create pool1/dataLoad the Monday tape and enter:zfs recv pool1/data </dev/rmt/0Load the Wednesday tape and enter:zfs recv –F pool1/data < /dev/rmt/0
- B. Load the Sunday tape and restore the Sunday snapshot:zfs recv pooll/data </dev/rmt/0zfs rollback pool1/data@monLoad the Wednesday tape and restore the Wednesday snapshot:zfs recv –i pooll/data < /dev/rmt/0zfs rollback pool1/data@wed
- C. zfs create pooll/dataLoad the Wednesday tape and enter:zfs recv -F pool1/data </dev/rmt/0
- D. Load the Sunday tape and enter:zfs recv pool1/data < /dev/rmt/0Load the Wednesday tape and enter:* commands missing*
Answer: D
Explanation: First the full backup must be restored. This would be the Sunday backup.
Then the last incremental backup must be restored. This would be the Wednesday backup. Before restoring the Wednesday incremental file system snapshot, the most recent snapshot must first be rolled back.
By exclusion D) would be best answer even though it is incomplete.
NEW QUESTION 3
Which two are user definable OpenBoot parameters that can be set in the OpenBoot PROM?
- A. IP address for the system console
- B. Host ID
- C. System date and time
- D. Default boot device
- E. Verbose hardware diagnostics
- F. Powering off the hardware
Answer: DE
Explanation: The NVRAM chip stores user-definable system parameters, also referred to as NVRAM variables or EEPROM parameters. The parameters allow administrators to control
variables such as the default boot device and boot command. The NVRAM also contains writeable areas for user-controlled diagnostics, macros, and device aliases. NVRAM is where the system identification information is stored, such as the host ID, Ethernet address, and time-of-day (TOD) clock.
Examples of NVRAM variables:
Variable Default Description boot-device disk or net The device from which to start up.
diag-device net The diagnostic startup source device.
diag-file Empty string Arguments passed to the startup program in diagnostic mode. diag-switch? false Whether to run in diagnostic mode
NEW QUESTION 4
Select the two statements that correctly describe the operation of NWAM.
- A. If a location is explicitly enabled, it remains active until explicitly changed.
- B. Wireless security keys can be configured by using the nwammgr command.
- C. NWAM stores profile information in /etc/ipadm/ipadm.conf and /etc/dladm/datalink.conf.
- D. Multiple locations may be automatically activated in systems with multiple network interface cards.
- E. Interface NCU Properties "float" and are automatically attached to the highest priority Link NCU Property.
- F. If the DefaultFixed NCP is enabled, persistent configuration, stored in /etc/ipadm.conf and /etc/dladm/datalink.conf is used.
Answer: AD
Explanation: A: Conditional and system locations can be manually activated, which means that the location remains active until explicitly disabled.
D: A location comprises certain elements of a network configuration, for example a name service and firewall settings, that are applied together, when required. You can create multiple locations for various uses. For example, one location can be used when you are connected at the office by using the company intranet. Another location can be used at home when you are connected to the public Internet by using a wireless access point. Locations can be activated manually or automatically, according to environmental conditions, such as the IP address that is obtained by a network connection.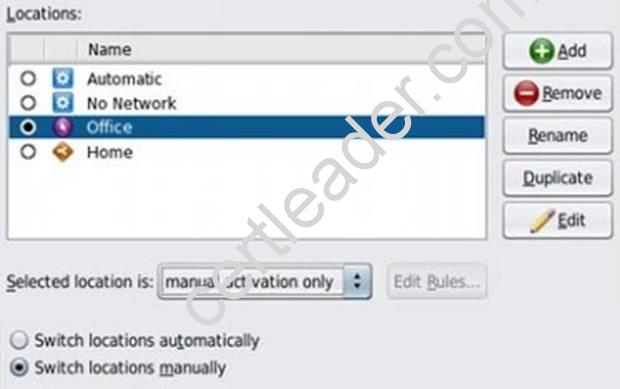
NEW QUESTION 5
In an effort to reduce storage space on your server, you would like to eliminate duplicate copies of data in your server’s ZFS file systems.
How do you specify that pool1/data should not contain duplicate data blocks (redundant data) on write operations?
- A. zfs create - o compression=on pool1/data
- B. zpool create -o deduplication =on pool1; zfs create pool1/data
- C. zfs create - o deduplication=on pool1; zfs create pool1/data
- D. zfs create - o dedupratio=2 pool1/data
- E. zfs create - o dedup=on pool1/data
Answer: E
Explanation: ZFS Deduplication Property
Solaris Express Community Edition, build 129: In this Solaris release, you can use the deduplication property to remove redundant data from your ZFS file systems. If a file system has the dedup property enabled, duplicate data blocks are removed synchronously. The result is that only unique data is stored and common components are shared between files.
You can enable this property as follows:
# zfs set dedup=on tank/home
NEW QUESTION 6
Which two statements describe the COMSTAR framework available in Oracle Solaris 11?
- A. It converts an Oracle Solaris 11 host into a SCSI target device that can be accessed over a storage network by Linux, Mac OS, or Windows client systems.
- B. iSCSI targets cannot be configured as dump devices.
- C. It provides support for iSCSI devices that use SLP.
- D. It is used to connect to Fibre Channel or iSCSI Storage Area Network (SAN) environments.
- E. It provides an upgrade and update path to convert your iSCSI LUNs from Solaris 10 systems.
Answer: AB
Explanation: A: You can configure Common Multiprotocol SCSI TARget, or COMSTAR, a software
framework that enables you to convert any Oracle Solaris 11 host into a SCSI target device that can be accessed over a storage network by initiator hosts.
This means you can make storage devices on a system available to Linux, Mac OS, or Windows client systems as if they were local storage devices. Supported storage protocols are iSCSI, FC, iSER, and SRP.
B: iSCSI targets cannot be configured as dump devices.
NEW QUESTION 7
To help with your troubleshooting, you need to determine the version of the OBP. Which two commands will provide you with this information?
- A. printenv
- B. banner
- C. .version
- D. set-env
- E. show-devs
- F. value version
Answer: BC
Explanation: B: banner
Displays power-on banner.
The PROM displays the system banner. The following example shows a SPARCstation 2 banner. The banner for your SPARC system may be different.
SPARCstation 2, Type 4 Keyboard
ROM Rev. 2.0, 16MB memory installed, Serial # 289 Ethernet address 8:0:20:d:e2:7b, Host ID: 55000121 C: .version
Displays version and date of the boot PROM.
Note: OBP-OpenBootProm is a firmware which is placed on the sun machine's prom chip. It is a os independent user interface to deal with the sun machine's hardware components. The user interface provides one or more commands to display system information.
NEW QUESTION 8
The core dump configuration in your non global zone is
A user is running a process in a non-global zone (testzone) and the process crashes. The process information is:
user126632618017:46:42pts/20:00/usr/bin/bash
When the user's process crashes in testzone, a non-global zone, where will the core dump be saved?
- A. The file will be stored in the non-global zone's directory:/var/core/pprocess/core.hash.2663.
- B. The file will be saved in the global zone's directory: /var/core/core.bash.2663.
- C. A core file cannot be generated in a non-global zone because it shares the kernel with the global zone.
- D. The file will be stored in the global zone's directory: /var/core/pprocess/core.bash.2663.
- E. The file will be saved in non-global zone’s directory: /var/core/core.bash.2663
Answer: E
Explanation: The line
init core file pattern: /var/core/core.%f.%p
will be used for the non-global process to determine the destination of the dump file.
Note: When a process is dumping core, up to three core files can be produced: one in the per-process location, one in the system-wide global location, and, if the process was running in a local (non-global) zone, one in the global location for the zone in which that process was running.
NEW QUESTION 9
What is the output of the following command, if executed using the default shell for the root role account of a standard Live CD Install of Oracle Solaris 11?
echo '$SHELL'
- A. /usr/bin/bash
- B. /usr/bin/ksh
- C. $SHELL
- D. the PID for the current shell
Answer: C
Explanation: Single quotes are most strict. They prevent even variable expansion. Double quotes prevent wildcard expansion but allow variable expansion. For example:
#!/bin/sh echo $SHELL
echo "$SHELL"
echo '$SHELL' This will print:
/usr/bin/bash
/usr/bin/bash
$SHELL
NEW QUESTION 10
To confirm the IP addresses and netmasks have been correctly configured on the network interfaces, which command(s) should you use?
- A. ipadm show-if
- B. ipadm show-nic
- C. ipadm show-addr
- D. ipadm show-addripadm show-mask
- E. ipadm show-ipipadm show-mask
- F. ipadm show-config
Answer: C
Explanation: Show address information, either for the given addrobj or all the address objects configured on the specified interface, including the address objects that are only in the persistent configuration.
Example:
# ipadm show-addr
ADDROBJ TYPE STATE ADDR
lo0/v4 static ok 127.0.0.1/8 lo0/v6 static ok ::1/128
NEW QUESTION 11
Which operation will fail if the DNS configuration is incorrect?
- A. domainname
- B. ping localhost.
- C. ping 192.168.1.1
- D. ping 23.45.82.174
- E. ping www.oracle.com.
- F. cat /etc/resolv.conf
Answer: E
Explanation: www.oracle.com would have to be resolved to an IP name by the domain name service.
NEW QUESTION 12
Select the five tasks that need to be performed on the Automated Installer (AI) install server before setting up the client.
- A. Create a local IPS repository on the AI Install server and start the repository server service, the publisher origin to the repository file.
- B. Set up a IP address on the AI install server.
- C. The DHCP server must be enabled on the install server and must provide the DHCP service for the clients.
- D. DHCP must be available on the network for the Install server and the clients, but the install server does not need to be the DHCP server.
- E. Download the AI boot imag
- F. The image must be the same version as the Oracle Solaris OS that you plan to install on the client.
- G. Download the text install image into the IPS repository.
- H. Install the AI installation tools.
- I. Create the AI install servic
- J. Specify the path to the AI network boot image ISO file and the path where the AI net image ISO file should be unpacked.
- K. Create the AI install servic
- L. Specify the path to the AI network boot image ISO file and the path to the IPS repository.
Answer: BDFGI
Explanation: B: Configure the AI install server to use a static IP address and default route.
D: The create-service command can set up DHCP on the AI install server. If you want to set up a separate DHCP server or configure an existing DHCP server for use with AI. The DHCP server must be able to provide DNS information to the systems to be installed.
E: An automated installation of a client over the network consists of the following high-level steps:
1. The client system boots over the network and gets its network configuration and the location of the install server from the DHCP server.
2. The install server provides a boot image to the client.
3. Characteristics of the client determine which installation instructions and which system configuration instructions are used to install the client.
4. The Oracle Solaris 11 OS is installed on the client, pulling packages from the package repository specified by the installation instructions in the AI install service.
G: Install the AI tool set.
Use the installadm create-service command to create an AI install service. Give the service a meaningful name, and specify the path where you want the service created. Specify the source of the network boot image (net image) package or ISO file.
installadm create-service [-n svcname] [-s FMRI_or_ISO] [-d imagepath]
-d imagepath
The imagepath is the location of the new install service. The install-image/solaris-auto- install package is installed to this location, or the specified ISO file is expanded at this location.
NEW QUESTION 13
Your SPARC server will not boot into multi user-server milestones and you need to troubleshoot to out why. You need to start the server with minimal services running so that you can go through each milestone manually to troubleshoot the issue.
Select the option that boots the server with the fewest services running.
- A. boot -s
- B. boot milestone none
- C. boot -m milestone=single-user
- D. boot -m milestone=none
- E. boot -m none
Answer: D
Explanation: The command boot -m milestone=none is useful in repairing a system that have problems booting early.
Boot Troubleshooting:
To step through the SMF portion of the boot process, start with: boot -m milestone=none
Then step through the milestones for the different boot levels: svcadm milestone svc:/milestone/single-user:default
svcadm milestone svc:/milestone/multi-user:default svcadm milestone svc:/milestone/multi-user-server:default
NEW QUESTION 14
Your are troubleshooting network throughput on your server.
To confirm that the load balancing among aggregated links is functioning properly, you want to examine the traffic statistics on the links comprising the aggregation.
The correct command is .
- A. dlstat - aggr
- B. dlstat show-aggr
- C. dlstat show-link -r
- D. dlstat show-link -aggr
- E. dlstat show-phys -aggr
Answer: B
Explanation: dlstat show-aggr [-r | -t] [-i interval] [-p] [ -o field[, ...]] [-u R|K|M|G|T|P] [link] Display per-port statistics for an aggregation.
NEW QUESTION 15
How should you permanently restrict the non-global zone testzone so that it does not use more than 20 CPU shares while it is running?
- A. While configuring the zone, add this entry:add rct1set name = capped.cpu-sharesadd value (priv = privileged, limit = 20, action = none)endexit
- B. While configuring the zone, add this entry: add rct1set name= zone.cpu-sharesadd value (priv=privileged, limit=20, action=none)endexitfrom command line, enter: # dispadmin- d FSS
- C. From the command line enter: #prct1 -n zone.cpu-shares - r - v 20 - i zone testzone
- D. From the command line, enter:#prct1 - n zone.cpu-shares - v 80 - r - i zone global
Answer: C
Explanation: The prctl utility allows the examination and modification of the resource controls associated with an active process, task, or project on the system. It allows access to the basic and privileged limits and the current usage on the specified entity.
How to Change the zone.cpu-shares Value in a Zone Dynamically This procedure can be used in the global zone or in a non-global zone.
For more information about roles, see Configuring and Using RBAC (Task Map) in System Administration Guide: Security Services.
# prctl -n zone.cpu-shares -r -v value -i zone zonename
idtype is either the zonename or the zoneid. value is the new value.
Note: project.cpu-shares
Number of CPU shares granted to a project for use with the fair share scheduler
NEW QUESTION 16
You have already generated a 256-bit AES raw key and named the keystore file /mykey. You need to use the key to create an encrypted file system.
Which command should you use to create a ZFS encrypted file system named pool1/encrypt using the /mykey keystore?
- A. zfs create - o encryption = /mykey pool1/encrypt
- B. zfs create - o encryption = 256-ccm - o keysource = raw, file : ///my key pool1/encrypt
- C. zfs create - o encryption = AES keysource = /mykey pool1/encrypt
- D. zfs create - o encryption = on keystore = /mykey pool1/encrypt
Answer: B
Explanation: Example: Encrypting a ZFS File System by Using a Raw Key
In the following example, an aes-256-ccm encryption key is generated by using the pktool command and is written to a file, /cindykey.file.
# pktool genkey keystore=file outkey=/cindykey.file keytype=aes keylen=256
Then, the /cindykey.file is specified when the tank/home/cindy file system is created.
# zfs create -o encryption=aes-256-ccm -o keysource=raw, file:///cindykey.file tank/home/cindys
NEW QUESTION 17
You are having an issue with the shutdown command. You wish to determine if the file is a script or an executable program. Which command would you use to determine this?
- A. od shutdown
- B. file shutdown
- C. test shutdown
- D. cksum shutdown
- E. attrib shutdown
Answer: B
Explanation: The file command determines the file type file tests each argument in an attempt to classify it. There are three sets of tests, performed in this order: filesystem tests, magic tests, and language tests. The first test that succeeds causes the file type to be printed.
NEW QUESTION 18
ServerA contains two ISO images of a package repository named so1.repo.iso-a and so1.repo.iso-b respectively. You need to create a single local package repository on server that clients can connect to. The package repository will be stored on the /export/IPS file system and named repo. The preferred publisher will be named solaris and the publisher URL will be http://serverA.example.com.
Which is the correct procedure to perform on ServerA to create the local Package repository?
- A. cat so1.repo.iso-a sol.repo.iso-b > so1.full.isoMount the ISO image and use the rsync command to extract the contents of the ISO file to the /export/IPS file system.Set the pkg/inst_root property to /export/IPS/repo and the pkg/readonly property to true.Set the preferred publisher by using pkg set-publisher -Ghttp://pkg.oracle.com/solaris/release/ -g http”//serverA.example.com/ solaris
- B. cat so1.repo.iso-a so1.repo.iso-b > /export/IPS/repoSet the pkg/inst_root property to true and the pkg/readonly property to /export/IPSSet the preferred publisher by using pkg set-publisher -G http://serverA.example.com/ -g http://pkg/oracle.com/solaris/rekease/solaris
- C. cat so1.repo.iso-a so1.repo.iso-b > so1.full.isoMount the ISO image and use the rsync command to extract the contents of the ISO file to /export/IPS/repoSet the pkg/inst_root property to /export/IPS/repo and the pkg/readonly property to trueSet the preferred publisher by using pkg set-publisher solaris -g http://pkg.oracle.com/
- D. cat so1.repo, iso-a so1.repo.iso-b > /export/IPS/repo.isoMount the ISO image and copy the repo directory from the ISO image to /export/IPS/reposet the pkg/inst_root property and the pkg/readonly property to /export/IPS/reposet the preferred pkg/inst_root property by using pkg set-publisher - G http://serverA.example.com/ - g http://pkg.oracle.com/solaris.com/release/- p solaris
Answer: A
Thanks for reading the newest 1Z0-821 exam dumps! We recommend you to try the PREMIUM Certshared 1Z0-821 dumps in VCE and PDF here: https://www.certshared.com/exam/1Z0-821/ (243 Q&As Dumps)