Free of 642-885 free practice questions materials and bible for Cisco certification for IT specialist, Real Success Guaranteed with Updated 642-885 pdf dumps vce Materials. 100% PASS Deploying Cisco Service Provider Advanced Routing (SPADVOUTE) exam Today!
Check 642-885 free dumps before getting the full version:
NEW QUESTION 1
Refer to the Cisco IOS DHCPv6 configuration shown in the exhibit.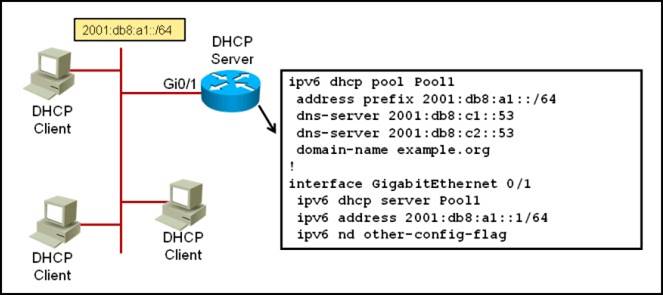
Which statement is correct?
- A. The configuration is missing a command under interface Gi0/1 to indicate to the attached hosts to use stateful DHCPv6 to obtain their IPv6 addresses
- B. The IPv6 router advertisements indicate to the attached hosts on the Gi0/1 interface to get other information besides their IPv6 address via stateless auto configuration
- C. The IPv6 DHCPv6 server pool configuration is misconfigured
- D. The DNS server address can also be imported from another upstream DHCPv6 server
Answer: A
Explanation:
Server Configuration
In Global Configuration Mode ipv6 unciast-routing
ipv6 dhcp pool <pool name>
address prefix <specify address prefix> lifetime <infinite> <infinite> dns-server <specify the dns server address>
domain-name <specify the domain name> exit
In Interface Configuration Mode
ipv6 address <specify IPv6 Address>
ipv6 dhcp server <server name>rapid-commit Client Configuration
In Global Configuration Mode enable
configure terminal ipv6 unicast-routing
In Interface Configuration Mode ipv6 address dhcp rapid commit ipv6 enable
exit
NEW QUESTION 2
Which of the following is a feature added in IGMPv3?
- A. Support for source filtering
- B. Support for Host Membership Report and a Leave Group message
- C. Uses a new variation of the Host Membership Query called the Group-Specific Host Membership Query
- D. Uses an election process to determine the querying router on the LAN
- E. Uses an election process to determine the designated router on the LAN
- F. IPv6 support
Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 3
Which multicast routing protocol is most optimal for supporting many-to-many multicast applications?
- A. PIM-SM
- B. PIM-BIDIR
- C. MP-BGP
- D. DVMRP
- E. MSDP
Answer: B
Explanation:
PIM-Bidirectional Operations
PIM Bidirectional (BIDIR) has one shared tree from sources to RP and from RP to receivers. This is unlike the PIM-SM, which is unidirectional by nature with multiple source trees - one per (S, G) or a shared tree from receiver to RP and multiple SG trees from RP to sources.
Benefits of PIM BIDIR are as follows:
• As many sources for the same group use one and only state (*, G), only minimal states are required in each router.
• No data triggered events.
• Rendezvous Point (RP) router not required. The RP address only needs to be a routable address and need not exist on a physical device.
NEW QUESTION 4
Refer to the exhibit.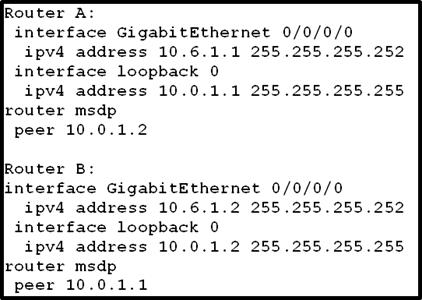
Router A and Router B are connected via GigabitEthernet interfaces, but they are unable to form an MSDP neighborship. Which two components must be addressed when fixing the MSDP peering issue? (Choose two.)
- A. An msdp default peer is configured on both routers.
- B. A BGP process on each router is present so that MSDP can peer and carry updates.
- C. The router interfaces are PIM-enabled to transport MSDP updates.
- D. The connect-source attribute is configured with a host route under the MSDP process.
- E. The MSDP peering on both routers specifies an origin ID so that it can peer.
- F. The router A loopback interface configures the correct subnet mask.
Answer: DF
NEW QUESTION 5
Given the IPv6 address of 2001:0DB8::1:800:200E:88AA, what will be its corresponding the solicited-node multicast address?
- A. FF01::1:200E:88AA
- B. FF01::1:FF0E:88AA
- C. FF01:0DB8::1:800:200E:88AA
- D. FF02::1:FF0E:88AA
- E. FF02::1:200E:88AA
- F. FF02:0DB8::1:800:200E:88AA
Answer: D
Explanation:
IPv6 nodes (hosts and routers) are required to join (receive packets destined for) the following multicast groups:
•All-nodes multicast group FF02:0:0:0:0:0:0:1 (scope is link-local)
•Solicited-node multicast group FF02:0:0:0:0:1:FF00:0000/104 for each of its assigned unicast and anycast addresses
IPv6 routers must also join the all-routers multicast group FF02:0:0:0:0:0:0:2 (scope is link- local).
The solicited-node multicast address is a multicast group that corresponds to an IPv6 unicast or anycast address. IPv6 nodes must join the associated solicited-node multicast group for every unicast and anycast address to which it is assigned. The IPv6 solicited- node multicast address has the prefix FF02:0:0:0:0:1:
FF00:0000/104 concatenated with the 24 low-order bits of a corresponding IPv6 unicast or anycast address (see Figure 2). For example, the solicited-node multicast address corresponding to the IPv6 address 2037::01:800:200E:8C6C is FF02::1:FF0E:8C6C. Solicited-node addresses are used in neighbor solicitation messages
NEW QUESTION 6
Refer to the exhibit.
Given the partial BGP configuration, which configuration correctly completes the Cisco IOS-XR route reflector configuration where both the 1.1.1.1 and 2.2.2.2 routers are the clients and the 3.3.3.3 router is a non-client IBGP peer?
- A. neighbor 1.1.1.1remote-as 65123 route-reflector-client neighbor 2.2.2.2remote-as 65123 route-reflector-client neighbor 3.3.3.3remote-as 65123
- B. neighbor 1.1.1.1 address-family ipv4 unicast remote-as 65123route-reflector-client neighbor 2.2.2.2address-family ipv4 unicast remote-as 65123route-reflector-client neighbor 3.3.3.3address-family ipv4 unicast remote-as 65123
- C. neighbor 1.1.1.1remote-as 65123address-family ipv4 unicast route-reflector-client neighbor 2.2.2.2remote-as 65123address-family ipv4 unicast route-reflector-client neighbor 3.3.3.3remote-as 65123
- D. neighbor 1.1.1.1 remote-as 65123neighbor 1.1.1.1 route-reflector-clientneighbor 2.2.2.2 remote-as 65123neighbor 2.2.2.2 route-reflector-clientneighbor 3.3.3.3 remote-as 65123
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 7
Refer to the exhibit.
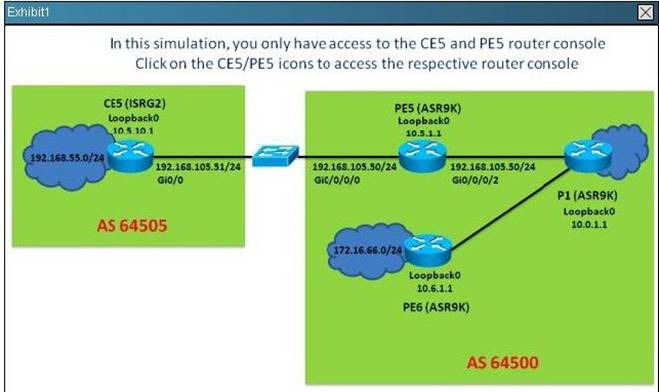
On the PE5 router, which statementis correct regarding the learned BGP prefixes?
- A. The 209.165.201.0/27 prefix is received from the 10.0.1.1 IBGP peer which is a route reflector
- B. The 172.16.66.0/24 prefix BGP next-hop points to the route reflector
- C. All prefixes learned on PE5 has the default local preference value
- D. The 209.165.202.128/27 prefix is originated by the 10.0.1.1 IBGP peer
Answer: C
Explanation:
#show ip bgp -- check i tag for PE5
NEW QUESTION 8
What are three BGP configuration characteristics of a multihomed customer that is connected to multiple service providers? (Choose three.)
- A. The multihomed customer can use local preference to influence the return traffic from the service providers
- B. The multihomed customer announces its assigned IP address space to its service providers through BGP
- C. The multihomed customer has to decide whether to perform load sharing or use a primary/backup implementation
- D. The multihomed customer must use private AS number
- E. The multihomed customer configures outbound route filters to prevent itself from becoming a transit AS
Answer: BCE
NEW QUESTION 9
Which two actions result when a network administrator attempts to ping an IPv6 host on the LAN? (Choose two.)
- A. ARP is used to determine the MAC address of the destination host.
- B. Neighbor Discovery is used to determine the MAC address of the destination host.
- C. Neighbor Solicitation messages are sent out by the source host to determine the data link-layer address of the destination host.
- D. Neighbor Advertisement messages are sent by the source host to announce its presence on the local link.
- E. Router Solicitation messages are sent out on a specific multicast address to request the data link-layer address of the target device.
- F. Router Solicitation messages are sent to the local router on the network segment to request data link-layer information about the destination host.
Answer: BC
NEW QUESTION 10
Which Cisco IOS XR command setssuccessfully configure a value of 20 for the advertisement-interval?
- A. RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:routerconfig)# router bgp 65512 RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp)# session-group test RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp-sngrp)# advertisement-interval 20 RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp-sngrp)# exit RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp)# neighbor-group test RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp-nbrgrp)# advertisement-interval 25 RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp-nbrgrp)# exit RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp)# exit RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp)# neighbor 192.168.1.1RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp-nbr)# remote-as 65513 RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp-nbr)# use session-group test RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp-nbr)# use neighbor-group test
- B. RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:routerconfig)# router bgp 65512 RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp)# session-group test RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp-sngrp)# ebgp-multihop 2 RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp-sngrp)# exit RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp)# neighbor-group test RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp-nbrgrp)# advertisement-interval 20 RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp-nbrgrp)# exit RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp)# exit RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp)# neighbor 192.168.1.1RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp-nbr)# remote-as 65513 RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp-nbr)# use session-group test RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp-nbr)# use neighbor-group test
- C. RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:routerconfig)# router bgp 65512 RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp)# session-group test RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp-sngrp)# exit RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp)# neighbor-group test RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp-nbrgrp)# exit RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp)# exit RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp)# neighbor 192.168.1.1RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp-nbr)# remote-as 65513 RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp-nbr)# use session-group test RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp-nbr)# use neighbor-group test
- D. RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:routerconfig)# router bgp 65512 RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp)# session-group test RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp-sngrp)# advertisement-interval 25 RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp-sngrp)# exit RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp)# neighbor-group test RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp-nbrgrp)# advertisement-interval 20 RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp-nbrgrp)# exit RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp)# exit RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp)# neighbor 192.168.1.1RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp-nbr)# remote-as 65513 RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp-nbr)# use session-group test RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp-nbr)# use neighbor-group test
Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 11
A service providerrequests more details about the recent Inter-AS MPLS VPN Option B configuration that was recently deployed. Consider this configuration:
router bgp 3717
address-family vpnv4 unicast retain route-target all
commit
!
Which option describes why this particular command is needed?
- A. The ASBRcan have many working customer VRFs, so this configuration ensures the coexistence of all the route-target extended communities that belong to the all ASBR- terminated customer VRFs.
- B. When implementing the Inter-AS Option B MPLS VPN solution, all the route targets that are transmitted over the Inter-AS links need an ASBR local database to forward thecustomer traffic correctly.
- C. The Inter-AS Option B design implements VPNv4 communication over the Inter-AS link, hence the requirement for a route-target association for each customer VPN connected across two or more ASs.
- D. In the Inter-AS Option B design, no local VRF is maintained on the ASBR routers,so the default behavior of the operating system is to deny any route-target extended community that is encoded in the incoming iBGP update
- E. This configuration permits VPNv4 communication by accepting the iBGP updates even if no route targets are configured locally.
Answer: D
NEW QUESTION 12
Which two statements correctly describe the RPF check when a multicast packet arrives at a router? (Choose two.)
- A. The router looks up the source address in the unicast routing table to determine if the packet has arrived on the interface that is on the reverse path back to the source
- B. The router looks up the destination address in the unicast routing table to determine if the packet has arrived on the interface that is on the reverse path back to the destination
- C. If the packet has arrived on the interface leading back to the destination, the RPF check passes and the packet is forwarde
- D. If the RPF check fails, the packet is dropped
- E. If the packet has arrived on the interface leading back to the source, the RPF check passes and the packet is forwarde
- F. If the RPF check fails, the packet is dropped
Answer: AD
Explanation:
Reverse Path Forwarding (RPF)
RPF is a fundamental concept in multicast routing that enables routers to correctly forward multicast traffic down the distribution tree. RPF makes use of the existing unicast routing table to determine the upstream and downstream neighbors. A router will only forward a multicast packet if it is received on the upstream interface.
This RPF check helps to guarantee that the distribution tree will be loop free. RPF Check
When a multicast packet arrives at a router, the router will perform an RPF check on the packet. If the RPF check is successful, the packet will be forwarded. Otherwise it will be dropped.
For traffic flowing down a source tree, the RPF check procedure works as follows:
Step 1. Router looks up the source address in the unicast routing table to determine if it has arrived on the interface that is on the reverse path back to the source.
Step 2. If packet has arrived on the interface leading back to the source, the RPF check is successful and the packet will be forwarded.
Step 3. If the RPF check in 2 fails, the packet is dropped.
NEW QUESTION 13
In secure multicast, which protocol is used to distribute secure keys to a multicast group?
- A. ISAKMP
- B. RSA
- C. IPsec
- D. GDOI
- E. SKIP
Answer: D
NEW QUESTION 14
A network engineer of an ISP using Cisco IOS XR routers wants to limit the number of prefixes that BGP peers can accept. To accomplish this task, the command maximum- prefix 1000 is used. Which two results of this configuration are expected? (Choose two.)
- A. A warning message displays by default when 750 prefixes are received.
- B. A warning message displays by default when 850 prefixes are received.
- C. A BGP peer resets when it receives 1001 prefixes.
- D. A BGP peer resets when it receives 1000 prefixes.
- E. A BGP peer ceases when it receives 1001 prefixes.
- F. A BGP peer ceases when it receives 1000 prefixes.
- G. The BGP peer tries to reestablish the session after one minute.
Answer: AE
NEW QUESTION 15
Which two features are used to provide high availability multicast? (Choose two.)
- A. BFD
- B. NSF/SSO
- C. PIM NSR
- D. PIM triggered join
- E. IGMP triggered report
- F. MSDP
Answer: BD
Explanation:
Triggered joins are sent when the primary or the secondary RPF information changes. No RPF change prunes are sent for MoFRR streams.
mofrr
To perform a fast convergence (multicast-only fast reroute, or MoFRR) of specified routes/flows when a failure is detected on one of multiple equal-cost paths between the router and the source, use the mofrr command under PIM configuration mode.
mofrr rib acl_name no rib acl_name
NEW QUESTION 16
Which IPv6 mechanism occurs between a provider edge router and the customer premises equipment router to allow an ISP to automate the process of assigning a block of IPv6 addresses to a customer for use within the customer network?
- A. Router Advertisement
- B. DHCPv6 Prefix Delegation
- C. DHCPv6 Lite
- D. Stateful DHCPv6
Answer: B
Explanation:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk872/technologies_configuration_example09186a0080b 8a116.shtml
NEW QUESTION 17
Refer to the exhibit.
The following multicast IP addresses map to which multicast MAC address?
- A. 01:00:5E:8A:00:01
- B. 01:00:5E:0A:00:01
- C. 01:00:5E:7A:00:01
- D. 01:00:5E:05:00:01
Answer: B
NEW QUESTION 18
A network engineer must deploy an iBGP-based cloud region configuration by means of templates to reduce the overall BGP CLI required. Which three commands represent a basic configuration for a BGP peer session template on a regular Cisco IOS instance? (Choose three.)
- A. template peer-session session-template-name
- B. remote-as as-number
- C. neighbor-family config template
- D. peer-family config template
- E. as-override
- F. timers keepalive-interval hold-time
Answer: ABF
NEW QUESTION 19
The 224.192.16.1 multicast IP address maps to which multicast MAC address?
- A. 01-00-5E-C0-10-01
- B. 01-00-5E-40-10-01
- C. 01-00-5E-00-10-01
- D. 01-00-5E-C0-16-01
Answer: B
Explanation:
Least significant 23 bits of IP address and pre-pend 01-00-5E
224 ignore
192 less 128 becomes 64 = 40
16 = 10
1 = 01
01-00-5E-40-10-01
NEW QUESTION 20
Each router (RTA, RTB, and RTC) has one iBGP adjacency with the route reflector router RTD. Router RTC has an iBGP route advertised by RTA, but the same route is missing from RTB. Thenetwork engineer verifies that route filtering does not deny the route advertisement. Which action corrects the problem?
- A. RTD(config-router)#neighbor 192.168.1.1 route-reflector-client RTD(config-router)#neighbor 192.168.1.1 description RTA RTD(config-router)#neighbor 192.168.1.2 route-reflector-client RTD(config-router)#neighbor 192.168.1.2 description RTB
- B. RTC(config-router)#neighbor 192.168.1.4 route-reflector-client RTC(config-router)#neighbor 192.168.1.4 description RTD
- C. RTA(config-router)#neighbor 192.168.1.4 route-reflector-client RTA(config-router)#neighbor 192.168.1.4 description RTDRTB(config-router)#neighbor 192.168.1.4 route-reflector-client RTB(config-router)#neighbor 192.168.1.4 description RTD
- D. RTB(config-router)#neighbor 192.168.1.3 route-reflector-client RTB(config-router)#neighbor 192.168.1.3 description RTC
- E. RTB(config-router)#neighbor 192.168.1.3 route-reflector-client RTB(config-router)#bgp cluster-id 192.168.1.2RTB(config-router)#no bgp client-to-client reflection
Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 21
Refer to the exhibit.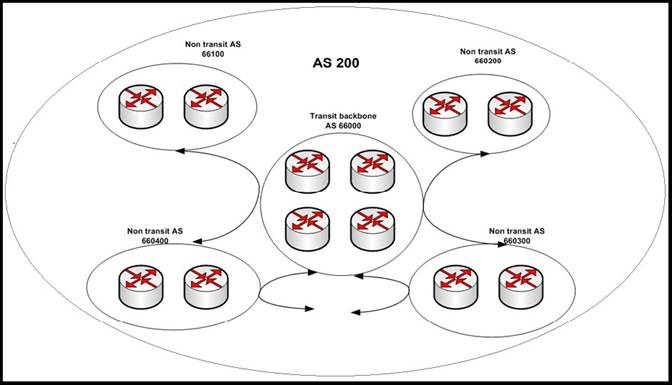
Which option is the function of designing a hub and spoke confederation?
- A. allows transit backbone area 66000 to be a blackhole for non-transit ASs
- B. reduces the iBGP mesh, iBGP mesh will be in sub non-transit ASs
- C. increases eBGP sessions between the confederation sub ASs
- D. allows transit backbone area and non-transit ASs to run the same IGP
Answer: B
NEW QUESTION 22
......
P.S. Certshared now are offering 100% pass ensure 642-885 dumps! All 642-885 exam questions have been updated with correct answers: https://www.certshared.com/exam/642-885/ (131 New Questions)