It is impossible to pass Microsoft 70-640 exam without any help in the short term. Come to us soon and find the most advanced, correct and guaranteed . You will get a surprising result by our .
Microsoft 70-640 Free Dumps Questions Online, Read and Test Now.
NEW QUESTION 1
You need to deactivate the UGMC option on some of your domain controllers.
At which level in Active Directory would you deactivate UGMC?
- A. Server
- B. Site
- C. Domain
- D. Forest
Answer: B
Explanation:
http://www.ntweekly.com/?p=788
http://gallery.technet.microsoft.com/scriptcenter/c1bd08d2-1440-40f8-95be-ad2050674d91 Script to Disable Universal Group Membership Caching in all Sites How to Disable Universal Group Membership Caching in all Sites using a Script Starting with Windows Server 2003, a new feature called Universal Group Membership Caching (UGMC) caches a user’s membership in Universal Groups on domain controllers authenticating the user. This feature allows a domain controller to have knowledge of Universal Groups a user is member of rather than contacting a Global Catalog.
Unlike Global group memberships, which are stored in each domain, Universal Group memberships are only stored in a Global Catalog. For example, when a user who belongs to a Universal Group logs on to a domain that is set to the Windows 2000 native domain functional level or higher, the Global Catalog provides Universal Group membership information for the user’s account at the time the user logs on to the domain to the authenticating domain controller.
UGMC is generally a good idea for multiple domain forests when:
1. Universal Group membership does not change frequently.
2. Low WAN bandwidth between Domain Controllers in different sites.
It is also recommended to disable UGMC if all Domain Controllers in a forest are Global
Catalogs.
NEW QUESTION 2
Your network contains an Active Directory forest named contoso.com. The forest contains a single domain. The domain contains two domain controllers named DC1 and DC2 that run Windows Server 2008 R2. DC1 is configured as the infrastructure master for contoso.com.
You need to move the infrastructure master role from DC1 to DC2.
What should you do?
- A. Run the dsadd.exe command
- B. Run the nltest.exe command
- C. Run the Set-AdDomain cmdle
- D. Run the dsmove.exe comman
- E. Run the dcpromo.exe comman
- F. Run the Move-AdDirectoryServer cmdle
- G. Use the Active Directory Schema snap-i
- H. Use the Active Directory Users and Computers consol
Answer: H
NEW QUESTION 3
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named contoso.com. All domain controllers run Windows Server 2008 R2. The domain contains a domain controller named DC1. DC1 hosts an Active Directory-integrated zone for contoso.com.
You enable record scavenging for contoso.com by using the default settings. You configure scavenging to run every seven days.
After 30 days, you discover that some DNS records of computers that were removed from the network are still present in the contoso.com zone.
You need to ensure that the scavenging process can remove the stale records.
What command should you run? (To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.) 
Answer:
Explanation: 
NEW QUESTION 4
A corporate network includes a single Active Directory Domain Services (AD D5) domain.
The HR department has a dedicated organization unit (OU) named HR. The HR OU has two sub-OUs: HR Users and HR Computers. User accounts for the HR department reside in the HR Users OU. Computer accounts for the HR department reside in the HR Computers OU. All HR department employees belong to a security group named HR Employees. All HR department computers belong to a security group named HR PCs.
Company policy requires that passwords are a minimum of six characters.
You need to ensure that, the next time HR department employees change their passwords, the passwords are required to have at least eight characters. The password length requirement should not change for employees of any other department.
What should you do?
- A. Create a fine-grained password policy and apply it to the HR Computers O
- B. Modify the password policy in the GPO that is applied to the domain controllers O
- C. Create a fine-grained password policy and apply it to the HR Employees grou
- D. Modify the password policy in the GPO that is applied to the domai
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 5
A corporate network includes a single Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) domain. All regular user accounts reside in an organizational unit (OU) named Employees. All administrator accounts reside in an OU named Admins.
You need to ensure that any time an administrator modifies an employee's name in AD DS, the change is audited.
What should you do first?
- A. Enable the Audit directory service access setting in the Default Domain Controllers Policy Group PolicyObjec
- B. Create a Group Policy Object with the Audit directory service access setting enabled and link it to the Employees O
- C. Enable the Audit directory service access setting in the Default Domain Policy Group Policy Objec
- D. Modify the searchFlags property for the User class in the schem
Answer: A
Explanation: http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc731607.aspx
In Windows 2000 Server and Windows Server 2003, there was one audit policy, Audit directory service access, that controlled whether auditing for directory service events was enabled or disabled. In Windows Server 2008, this policy is divided into four subcategories:
Directory Service Access Directory Service Changes Directory Service Replication Detailed Directory Service Replication
This step includes procedures to enable change auditing with either the Windows interface or a command line:
By using Group Policy Management, you can turn on the global audit policy, Audit directory service access, which enables all the subcategories for AD DS auditing.
To enable the global audit policy using the Windows interface
1. Click Start, point to Administrative Tools, and then Group Policy Management.
2. In the console tree, double-click the name of the forest, double-click Domains, double-click the name of your domain, double-click Domain Controllers, right-click Default Domain Controllers Policy, and then click Edit.
3. Under Computer Configuration, double-click Policies, double-click Windows Settings, double-click Security Settings, double-click Local Policies, and then click Audit Policy.
4. In the details pane, right-click Audit directory service access, and then click Properties.
5. Select the Define these policy settings check box.
6. Under Audit these attempts, select the Success, check box, and then click OK.
NEW QUESTION 6
Your network contains a server named Server1 that runs Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard. Server1 has the Active Directory Certificate Services (AD CS) role installed.
You configure a certificate template named Template1 for autoenrollment.
You discover that certificates are not being issued to any client computers. The event logs on the client computers do not contain any autoenrollment errors.
You need to ensure that all of the client computers automatically receive certificates based on Template1.
What should you do?
- A. Modify the Default Domain Policy Group Policy object (GPO).
- B. Modify the Default Domain Controllers Policy Group Policy object (GPO).
- C. Upgrade Server1 to Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterpris
- D. Restart Certificate Services on Server1.
Answer: A
Explanation: http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc731522.aspx
Configure Certificate Autoenrollment
Many certificates can be distributed without the client even being aware that enrollment is taking place. These can include most types of certificates issued to computers and services, as well as many certificates issued to users.
To automatically enroll clients for certificates in a domain environment, you must:
Configure a certificate template with Autoenroll permissions.
Configure an autoenrollment policy for the domain.
To configure autoenrollment Group Policy for a domain
1. On a domain controller running Windows Server 2008 R2 or Windows Server 2008, click Start, point to
Administrative Tools, and then click Group Policy Management.
2. In the console tree, double-click Group Policy Objects in the forest and domain containing the Default
Domain Policy Group Policy object (GPO) that you want to edit.
NEW QUESTION 7
Your network contains an Active Directory domain. The domain contains several domain controllers. All domain controllers run Windows Server 2008 R2.
You need to restore the Default Domain Policy Group Policy object (GPO) to the Windows Server 2008 R2 default settings.
What should you do?
- A. Run dcgpofix.exe /target:d
- B. Run dcgpofix.exe /target:domai
- C. Delete the link for the Default Domain Controllers Policy, and then run gpupdate.exe /forc
- D. Delete the link for the Default Domain Controllers Policy, and then run gpupdate.exe /syn
Answer: B
NEW QUESTION 8
Your network consists of an Active Directory forest that contains two domains. All servers run Windows Server 2008 R2. All domain controllers are configured as DNS Servers.
You have a standard primary zone for dev.contoso.com that is stored on a member server.
You need to ensure that all domain controllers can resolve names from the dev.contoso.com zone.
What should you do?
- A. On the member server, create a stub zon
- B. On the member server, create a NS record for each domain controlle
- C. On one domain controller, create a conditional forwarde
- D. Configure the conditional forwarder to replicate to all DNS servers in the fores
- E. On one domain controller, create a conditional forwarde
- F. Configure the conditional forwarder to replicate to all DNS servers in the domai
Answer: C
Explanation:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc730756.aspx Understanding Forwarders
A forwarder is a Domain Name System (DNS) server on a network that forwards DNS queries for external DNS names to DNS servers outside that network. You can also forward queries according to specific domain names using conditional forwarders. You designate a DNS server on a network as a forwarder by configuring the other DNS servers in the network to forward the queries that they cannot resolve locally to that DNS server. By using a forwarder, you can manage name resolution for names outside your network, such as names on the Internet, and improve the efficiency of name resolution for the computers in your network. The following figure illustrates how external name queries are directed with forwarders. 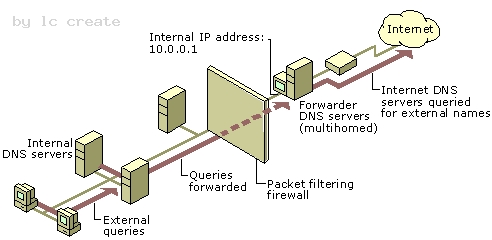
C:Documents and Settingsusernwz1Desktop1.PNG
Conditional forwarders A conditional forwarder is a DNS server on a network that forwards DNS queries according to the DNS domain name in the query. For example, you can configure a DNS server to forward all the queries that it receives for names ending with corp.contoso.com to the IP address of a specific DNS server or to the IP addresses of multiple DNS servers. Further information:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc794735%28v=ws.10%29.aspx Assign a Conditional Forwarder for a Domain Name http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc754941.aspx Configure a DNS Server to Use Forwarders
NEW QUESTION 9
Your company has two offices. The offices are located in Miami and London.
The network contains an Active Directory forest named contoso.com. The forest contains two child domains named miami.contoso.com and london.contoso.com. The domain contains 50 domain controllers that run Windows Server 2008 R2. Each office is configured as an Active Directory site.
You plan to deploy several read-only domain controllers (RODCs) to the Miami site.
You need to pre-create the computer accounts of the RODCs.
What should you do?
- A. Run the dsadd.exe command
- B. Run the nltest.exe comman
- C. Run the Set-AdDomain cmdle
- D. Run the dsmove.exe comman
- E. Run the dcpromo.exe comman
- F. Run the Move-AdDirectoryServer cmdle
- G. Use the Active Directory Schema snap-i
- H. Use the Active Directory Users and Computers consol
Answer: H
NEW QUESTION 10
Your company has an Active Directory forest. The forest includes organizational units corresponding to the following four locations:
. London
. Chicago
. New York
. Madrid
Each location has a child organizational unit named Sales. The Sales organizational unit contains all the users and computers from the sales department.
The offices in London, Chicago, and New York are connected by T1 connections. The office in Madrid is connected by a 256-Kbps ISDN connection.
You need to install an application on all the computers in the sales department.
Which two actions should you perform? (Each correct answer presents part of the solution. Choose two.)
- A. Create a Group Policy Object (GPO) named OfficeInstall that assigns the application to user
- B. Link the GPO to each Sales organizational uni
- C. Disable the slow link detection setting in the Group Policy Object (GPO).
- D. Configure the slow link detection threshold setting to 1,544 Kbps (T1) in the Group Policy Object (GPO).
- E. Create a Group Policy Object (GPO) named OfficeInstall that assigns the application to the computer
- F. Link the GPO to each Sales organizational uni
Answer: BD
Explanation:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc781031%28v=ws.10%29.aspx Specifying Group Policy for Slow Link Detection Administrators can partially control which Group Policy extensions are processed over a slow link. By default, when processing over a slow link, not all components of Group Policy are processed. Table 2.6 shows the default settings for processing Group Policy over slow links. 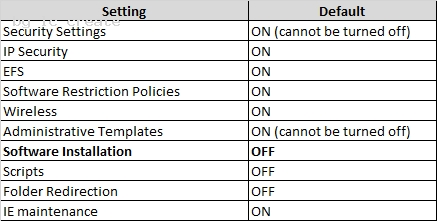
C:Documents and Settingsusernwz1Desktop1.PNG
Administrators can use a Group Policy setting to define a slow link for the purposes of applying and updating Group Policy. The default value defines a rate slower than 500 Kbps as a slow link. http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc783635%28v=ws.10%29.aspx Assigning and Publishing Software
Assigning software to computers After you assign a software package to computers in a site, domain, or OU, the software is installed the next time the computer restarts or the user logs on. Further information: http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc978717.aspx Group Policy slow link detection
NEW QUESTION 11
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named contoso.com.
You have a comma separated value (CSV) file named Users.txt. Users.txt contains the information for 500 users and all of the attributes required to create user accounts.
You plan to automate the creation of user accounts by using the Users.txt file.
You need to identify which two cmdlets you must run. The solution must pipe the output from the first cmdlet to the second cmdlet.
What should you run from Windows PowerShell? To answer, configure the appropriate PowerShell command in the answer area. 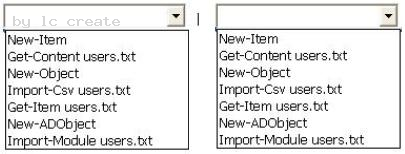
Answer:
Explanation: 
NEW QUESTION 12
Your network consists of a single Active Directory domain. User accounts for engineering department are located in an OU named Engineering.
You need to create a password policy for the engineering department that is different from your domain password policy.
What should you do?
- A. Create a new GP
- B. Link the GPO to the Engineering O
- C. Create a new GP
- D. Link the GPO to the domai
- E. Block policy inheritance on all OUs except for the Engineering O
- F. Create a global security group and add all the user accounts for the engineering department to the grou
- G. Create a new Password Policy Object (PSO) and apply it to the grou
- H. Create a domain local security group and add all the user accounts for the engineering department to the grou
- I. From the Active Directory Users and Computer console, select the group and run the Delegation of Control Wizar
Answer: C
Explanation:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc736813(WS.10).aspx
TechNet: Linking GPOs
If you need to modify some of the settings contained in the Default Domain Policy GPO, it is recommended that you create a new GPO for this purpose, link it to the domain, and set the Enforce option.
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc779159(WS.10).aspx
TechNet: Establishing Group Policy Operational Guidelines
Do not modify the default domain policy or default domain controller policy unless necessary. Instead, create a new GPO at the domain level and set it to override the default settings in the default policies.
Step 2
Edit the “Domain Password Policy” GPO and go to Computer Configurations>Policies>Windows
Settings>Security Settings>Account Policy>Password Policy and configured the password policies settings to the configuration you desire.
C:Documents and Settingsusernwz1Desktop1.PNG
Step 3
Once you have configured the password policy settings make the “Domain Password Policy” GPO the highest in the Linked GPO processing order.
TIP: Make sure you inform all your users when you are going to do this as it may trigger them to change their password the next time they logon.
C:Documents and Settingsusernwz1Desktop1.PNG
Done… told you it was easy….
Note: Even if you apply the password policies to the “Domain Controllers” OU it will not modify the domain’s password policy. As far as I know this is the only exception to the rule as to how GPO’s apply to objects. As you can see in the image below the “Minimum password length” in the “Domain Password Policy” GPO is still applied to the domain controller even though I have another GPO linking to the “Domain Controllers” OU configuration the same setting.
C:Documents and Settingsusernwz1Desktop1.PNG
For a better explanation as to why the GPO that is linked to the Domain and not the Domain Controllers is used for the password policy for all users check out Jorge’s Quest for Knowledge! – Why GPOs with Password and Account Lockout Policy Settings must be linked to the AD domain object to be affective on AD domain user accounts (http://blogs.dirteam.com/blogs/jorge/archive/2008/12/16/why-gpos-with-password-and-accountlockout- policy-settings-must-be-linked-to-the-ad-domain-object-to-be-affective-on-ad-domain-useraccounts.aspx)
How to set a Fine Grain Password Policy
Fine Grain Password Policies (FGPP) were introduced as a new feature of Windows Server 2008. Before this the only way to have different password polices for the users in your environment was to have separate domains… OUCH!
Pre-Requisites/Restrictions
You domain must be Windows Server 2008 Native Mode, this means ALL of your domain controllers must be running Windows Server 2008 or later. You can check this by selection the “Raise domain functional level” on the top of the domain in Active Directory Users and Computers.
C:Documents and Settingsusernwz1Desktop1.PNG
Explanation http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc770394(WS.10).aspx AD DS: Fine-Grained Password Policies The domain functional level must be Windows Server 2008. The other restriction with this option is that you can only apply FGPP to users object or
users in global security groups (not computers). Explanation http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc770394(WS.10).aspx AD DS: Fine-Grained Password Policies Fine-grained password policies apply only to user objects … and global security groups. TIP: If you setup an “Automatic Shadow Group
(http://policelli.com/blog/archive/2008/01/15/manage-shadowgroups-in-windows-server-2008/)” you can apply these password policies to users automatically to
any users located in an OU.
Creating a Password Setting Object (PSO)
Step 1 Under Administrator Tools Open ADSI Edit and connect it to a domain and domain controller you want to setup the new password policy.
C:Documents and Settingsusernwz1Desktop1.PNG
Note: If you do not see this option go to “Turn Windows Features On or Off” and make sure the “AD DS and AD LDS Tools” are installed. (You will need RSAT also installed if you are on Windows 7).
Step 2 Double click on the “CN=DomainName” then double click on “CN=System” and then double click on “CN=Password Settings Container”.
C:Documents and Settingsusernwz1Desktop1.PNG
Step 3
Right click on “CN=Password Settings Container” and then click on “New” then “Object.
C:Documents and Settingsusernwz1Desktop1.PNG
Step 4
Click on “Next”
C:Documents and Settingsusernwz1Desktop1.PNG
Step 5
Type the name of the PSO in the “Value” field and then click “Next”
C:Documents and Settingsusernwz1Desktop1.PNG
Note: With the exception of the password length the following values are all the same as the default values in the “Default Domain Policy”.
Step 6
Type in a number that will be the Precedence for this Password Policy then click “Next”.
Note: This is used if a users has multiple Password Settings Object (PSO) applied to them.
C:Documents and Settingsusernwz1Desktop1.PNG
Step 7
Type “FALSE” in the value field and click “Next”
Note: You should almost never use “TRUE” for this setting.
C:Documents and Settingsusernwz1Desktop1.PNG
Step 8
Type “24” in the “Value” field and click “Next”
C:Documents and Settingsusernwz1Desktop1.PNG
Step 9
Type “TRUE” in the “Value” field and click “Next”
C:Documents and Settingsusernwz1Desktop1.PNG
Step 10
Type “5” in the “Value” field and click “Next”
C:Documents and Settingsusernwz1Desktop1.PNG
Step 11
Type “1:00:00:00” in the “Value” field and click “Next”
C:Documents and Settingsusernwz1Desktop1.PNG
Step 12
Type “42:00:00:00” in the “Value” field and click “Next” C:Documents and Settingsusernwz1Desktop1.PNG Step 13
Type “10” in the “Value” field and click “Next” C:Documents and Settingsusernwz1Desktop1.PNG Step 14
Type “0:00:30:00” field and click “Next” C:Documents and Settingsusernwz1Desktop1.PNG Step 15
Type “0:00:33:00” in the “Value” field and click “Next” C:Documents and Settingsusernwz1Desktop1.PNG Step 16
Click “Finish”
C:Documents and Settingsusernwz1Desktop1.PNG
You have now created the Password Settings Object (PSO) and you can close the
ADSIEdit tool.
Now to apply the PSO to a users or group…
Step 17
Open Active Directory Users and Computers and navigate to “System > Password Settings
Container”
Note: Advanced Mode needs to be enabled.
C:Documents and Settingsusernwz1Desktop1.PNG
Step 18
Double click on the PSO you created then click on the “Attribute Editor” tab and then select the “msDS-PSOAppliedTo” attribute and click “Edit”
C:Documents and Settingsusernwz1Desktop1.PNG
Step 19
Click “Add Windows Accounts….” button.
C:Documents and Settingsusernwz1Desktop1.PNG
Step 20
Select the user or group you want to apply this PSO and click “OK”
C:Documents and Settingsusernwz1Desktop1.PNG
Step 21
Click “OK”
C:Documents and Settingsusernwz1Desktop1.PNG
Step 22
Click “OK”
C:Documents and Settingsusernwz1Desktop1.PNG
And your are done… (told you it was hard).
Fine Grain Password Policies as you can see are very difficult to setup and manage so it is probably best you use them sparingly in your organisation… But if you really have to have a simple password or extra complicated password then at least it give you away to do this without having to spin up another domain.
NEW QUESTION 13
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named contoso.com.
The domain contains an organizational unit (OU) named SalesUsers. The OU contains 50 user accounts. You need to identify the effective Password Settings object (PSO) of each user in the SalesUsers OU.
Which command should you run? (To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.) 
Answer:
Explanation: 
NEW QUESTION 14
Your network contains an Active Directory forest. The forest contains a single domain.
You want to access resources in a domain that is located in another forest.
You need to configure a trust between the domain in your forest and the domain in the other forest.
What should you create?
- A. an incoming external trust
- B. an incoming realm trust
- C. an outgoing external trust
- D. an outgoing realm trust
Answer: A
Explanation:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc816877.aspx
A one-way, incoming, external trust allows users in your domain (the domain that you are logged on to at the time that you run the New Trust Wizard) to access resources in another Active Directory domain (outside your forest).
NEW QUESTION 15
Your network contains an Active Directory forest named contoso.com.
The forest contains an enterprise certification authority (CA). The enterprise CA is inaccessible from the internet.
You have a server named Server1 that runs Windows Server 2008 R2. Server1 is accessible from the Internet. Server1 can communicate with the enterprise CA.
You need to ensure that laptops that are joined to the domain can renew their certificates automatically from the Internet.
Which two role services should you install on Server1? (To answer, select the two appropriate role services in the answer area.) 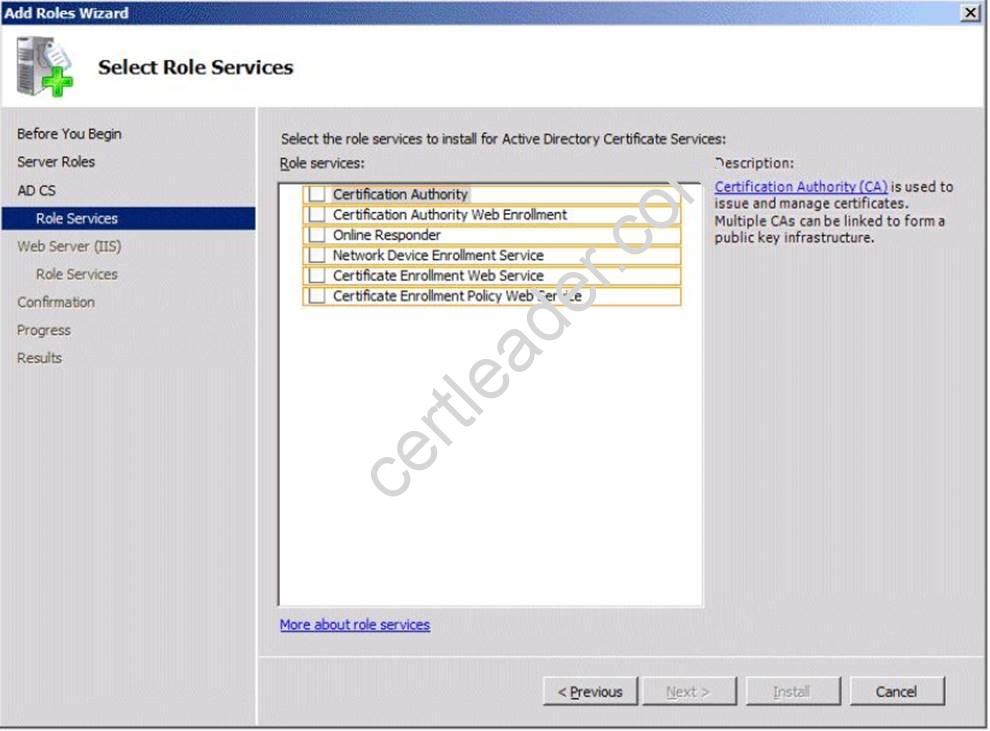
Answer:
Explanation: 
NEW QUESTION 16
DRAG DROP
Your network contains an Active Directory forest named contoso.com.
All client computers used by the sales department are in an organizational unit (OU) named Sales Computers. All user accounts for the sales department are in an OU named Sales Users.
You purchase a new application.
You need to ensure that every user in the domain who logs on to a sales department computer can use the application. The application must only be available from the sales department computers.
What should you do?
To answer, move the appropriate actions from the Possible Actions list to the Necessary Actions area and arrange them in the correct order. 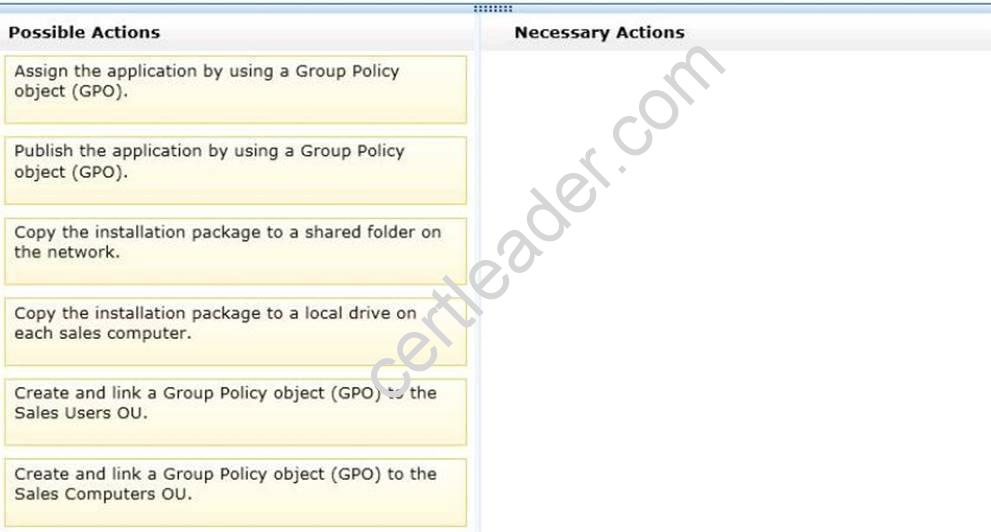
Answer:
Explanation: 
NEW QUESTION 17
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named contoso.com.
You need to create one password policy for administrators and another password policy for all other users.
Which tool should you use?
- A. Ntdsutil
- B. Active Directory Users and Computers
- C. ADSI Edit
- D. Group Policy Management Console (GPMC)
Answer: C
Explanation:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-US/library/cc754461.aspx
Creating a PSO using ADSI Edit
Active Directory Service Interfaces Editor (ADSI Edit) provides a view of every object and attribute in an Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) forest. You can use ADSI Edit to query, view, and edit AD DS objects and attributes.
To create a PSO using ADSI Edit
1. Click Start, click Run, type adsiedit.msc, and then click OK.
2. In the ADSI Edit snap-in, right-click ADSI Edit, and then click Connect to.
3. In Name, type the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) of the domain in which you want to create the PSO, and then click OK.
4. Double-click the domain.
5. Double-click DC=<domain_name>.
6. Double-click CN=System.
7. Click CN=Password Settings Container. All the PSO objects that have been created in the selected domain appear.
8. Right-click CN=Password Settings Container, click New, and then click Object.
9. In the Create Object dialog box, under Select a class, click msDS-PasswordSettings, and then click Next.
10. In Value, type the name of the new PSO, and then click Next.
11. Continue with the wizard, and enter appropriate values for all mustHave attributes.
NEW QUESTION 18
Your company Datum Corporation, has a single Active Directory domain named intranet.adatum.com. The domain has two domain controllers that run Windows Server 2008 R2 operating system. The domain controllers also run DNS servers.
The intranet.adatum.com DNS zone is configured as an Active Directory-integrated zone with the Dynamic updates setting configured to Secure only.
A new corporate security policy requires that the intranet.adatum.com DNS zone must be updated only by domain controllers or member servers.
You need to configure the intranet.adatum.com zone to meet the new security policy requirement.
Which two actions should you perform? (Each correct answer presents part of the solution. Choose two.)
- A. Remove the Authenticated Users account from the Security tab of the intranet.adatum.com DNS zone propertie
- B. Assign the SELF Account Deny on Write permission on the Security tab of the intranet.adatum.com DNS zone propertie
- C. Assign the server computer accounts the Allow on Write All Properties permission on the Security tab of the intranet.adatum.com DNS zone propertie
- D. Assign the server computer accounts the Allow on Create All Child Objects permission on the Security tab of the intranet.adatum.com DNS zone propertie
Answer: AD
Explanation:
http://www.advicehow.com/managing-dns-dynamic-updates-in-windows-server-2008-r2/ Managing DNS Dynamic Updates in Windows Server 2008 R2 What Is DNS Dynamic Update? When a DNS server is installed in a network, during the installation administrators can configure it to accept dynamic updates of client records. Dynamic updates means that DNS client computers can automatically register their names along with their IP addresses in the DNS server. When this happens DNS server automatically creates a Host (A) record for that client computer that contains hostname of the client and its associated IP address. Also, during the installation of DNS server administrators can choose an option according to which DNS server should not automatically update its records and in this condition administrators must manually create Host (A) records in the DNS database. http://www.windowsecurity.com/articles-tutorials/windows_server_2008_security/DNS-
Security-Part2.html
DNS Security (Part 2): DNS Security Steps Prior to Deploying DNSSEC In this article, then, we’ll take a look at the details of the following preliminary steps you can take to help secure your Windows DNS infrastructure: Decide who can resolve Internet host names Don’t co-locate internal and external zones Lock down the DNS cache Enable recursion only where needed Restrict DNS servers to listen on specific addresses Consider using a private root hints file Randomize your DNS source ports Be aware of the Global Query Block List Limit zone transfers Take advantage of Active Directory integrated zone security
Take advantage of Active Directory integrated zone security Active Directory integrated zones enable you to secure the registration of resource records when dynamic name registration is enabled. Members of the Active Directory domain can register their resource records dynamically while non-domain members will be unable to register their names. You can also use discretionary access control lists (DACLs) to control which computers are able to register or change their addressing information. The figure below shows how you configure secure dynamic updates. 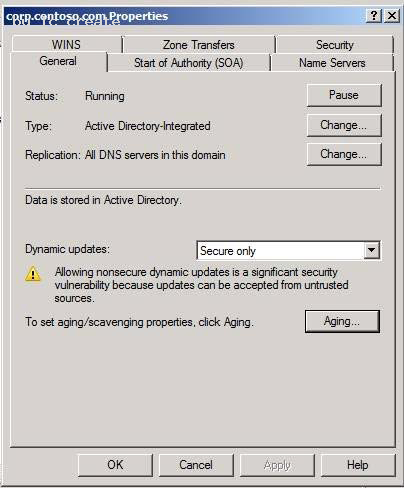
C:Documents and Settingsusernwz1Desktop1.PNG
http://www.tutorialspoint.com/shorttutorials/configuring-dns-server-for-secure-only-dynamic-updates/ Configuring DNS Server for Secure Only Dynamic Updates
Thanks for reading the newest 70-640 exam dumps! We recommend you to try the PREMIUM 2passeasy 70-640 dumps in VCE and PDF here: https://www.2passeasy.com/dumps/70-640/ (631 Q&As Dumps)