Highest Quality of 2V0-41.23 free exam questions materials and sample question for VMware certification for candidates, Real Success Guaranteed with Updated 2V0-41.23 pdf dumps vce Materials. 100% PASS VMware NSX 4.x Professional exam Today!
Check 2V0-41.23 free dumps before getting the full version:
NEW QUESTION 1
Which command is used to display the network configuration of the Tunnel Endpoint (TEP) IP on a bare metal transport node?
- A. tepconfig
- B. ifconfig
- C. tcpdump
- D. debug
Answer: B
Explanation:
The command ifconfig is used to display the network configuration of the Tunnel Endpoint (TEP) IP on a ba metal transport node2. The TEP IP is assigned to a network interface on the bare metal server that is used for overlay traffic. The ifconfig command can show the IP address, netmask, broadcast address, and other information of the network interface. For example, the following command shows the network configuration
of the TEP IP on a bare metal transport node with interface name ens192:
ifconfig ens192
The output of the command would look something like this:
ens192: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500 inet 10.10.10.10 netmask 255.255.255.1 broadcast 10.10.10.255 inet6 fe80::250:56ff:fe9a:1b8c prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20<link> ether 00:50:56:9a:1b:8c txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet) RX packets 123456 bytes 123456789 (123.4 MB) RX errors 0
dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0 TX packets 234567 bytes 234567890 (234.5 MB) TX errors 0 dropped 0
overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
The TEP IP in this example is 10.10.10.10. References: IBM Cloud Docs
IBM Cloud Docs
NEW QUESTION 2
An architect receives a request to apply distributed firewall in a customer environment without making changes to the network and vSphere environment. The architect decides to use Distributed Firewall on VDS.
Which two of the following requirements must be met in the environment? (Choose two.)
- A. vCenter 8.0 and later
- B. NSX version must be 3.2 and later
- C. NSX version must be 3.0 and later
- D. VDS version 6.6.0 and later
Answer: BD
Explanation:
Distributed Firewall on VDS is a feature of NSX-T Data Center that allows users to install Distributed Security for vSphere Distributed Switch (VDS) without the need to deploy an NSX Virtual Distributed Switch (N-VDS). This feature provides NSX security capabilities such as Distributed Firewall (DFW), Distributed IDS/IPS, Identity Firewall, L7 App ID, FQDN Filtering, NSX Intelligence, and NSX Malware Prevention. To enable this feature, the following requirements must be met in the environment: The NSX version must be 3.2 and later1. This is the minimum version that supports Distributed Security for VDS.
The NSX version must be 3.2 and later1. This is the minimum version that supports Distributed Security for VDS. The VDS version must be 6.6.0 and later1. This is the minimum version that supports the NSX host preparation operation that activates the DFW with the default rule set to allow.
The VDS version must be 6.6.0 and later1. This is the minimum version that supports the NSX host preparation operation that activates the DFW with the default rule set to allow.
References: Overview of NSX IDS/IPS and NSX Malware Prevention
Overview of NSX IDS/IPS and NSX Malware Prevention
NEW QUESTION 3
An NSX administrator would like to create an L2 segment with the following requirements:
• L2 domain should not exist on the physical switches.
• East/West communication must be maximized as much as possible.
Which type of segment must the administrator choose?
- A. VLAN
- B. Overlay
- C. Bridge
- D. Hybrid
Answer: B
Explanation:
An overlay segment is a layer 2 broadcast domain that is implemented as a logical construct in the NSX-T Data Center software. Overlay segments do not require any configuration on the physical switches, and they allow for optimal east/west communication between workloads on different ESXi hosts. Overlay segments use the Geneve protocol to encapsulate and decapsulate traffic between the hosts. Overlay segments are created and managed by the NSX Manager.
https://docs.vmware.com/en/VMware-NSX-T-Data-Center/3.2/administration/GUID-316E5027-E588-455C-88
NEW QUESTION 4
An administrator wants to validate the BGP connection status between the Tier-O Gateway and the upstream physical router.
What sequence of commands could be used to check this status on NSX Edge node?
- A. set vrf <ID>show logical-routers show <LR-D> bgp
- B. show logical-routers get vrfshow ip route bgp
- C. get gateways vrf <number>get bgp neighbor
- D. enable <LR-D> get vrf <ID>show bgp neighbor
Answer: C
Explanation:
The sequence of commands that could be used to check the BGP connection status between the Tier-O Gateway and the upstream physical router on NSX Edge node is get gateways, vrf <number>, get bgp neighbor. These commands can be executed on the NSX Edge node CLI after logging in as admin6. The firs command, get gateways, displays the list of logical routers (gateways) configured on the Edge node, along with their IDs and VRF numbers7. The second command, vrf <number>, switches to the VRF context of the desired Tier-O Gateway, where <number> is the VRF number obtained from the previous command7. The third command, get bgp neighbor, displays the BGP neighbor summary for the selected VRF, including the neighbor IP address, AS number, state, uptime, and prefixes received8. The other options are incorrect because they either use invalid or incomplete commands or do not switch to the correct VRF
context. References: NSX-T Command-Line Interface Reference, NSX Edge Node CLI Commands, Troubleshooting BGP on NSX-T Edge Nodes
NEW QUESTION 5
Which two BGP configuration parameters can be configured in the VRF Lite gateways? (Choose two.)
- A. Graceful Restart
- B. BGP Neighbors
- C. Local AS
- D. Route Distribution
- E. Route Aggregation
Answer: BD
Explanation:
According to the VMware NSX Documentation1, you can configure BGP neighbors for VRF-Lite by specifying the neighbor IP address, remote AS number, source IP address, and route filter. You can also configure route distribution for VRF-Lite by selecting the route redistribution sources and the route map to apply.
https://docs.vmware.com/en/VMware-NSX-T-Data-Center/3.2/administration/GUID-4CB5796A-1CED-4F0E-A
NEW QUESTION 6
An NSX administrator is reviewing syslog and notices that Distributed Firewall Rules hit counts are not being logged.
What could cause this issue?
- A. Syslog is not configured on the ESXi transport node.
- B. Zero Trust Security is not enabled.
- C. Syslog is not configured on the NSX Manager.
- D. Distributed Firewall Rule logging is not enabled.
Answer: D
NEW QUESTION 7
Which three selections are capabilities of Network Topology? (Choose three.)
- A. Display how the different NSX components are interconnected.
- B. Display the uplink configured on the Tier-0 Gateways.
- C. Display how the Physical components ate interconnected.
- D. Display the VMs connected to Segments.
- E. Display the uplinks configured on the Tier-1 Gateways.
Answer: ABD
Explanation:
According to the VMware NSX Documentation, these are three of the capabilities of Network Topology, which is a graphical representation of your network infrastructure in NSX: Display how the different NSX components are interconnected: You can use Network Topology to view how your segments, gateways, routers, firewalls, load balancers, VPNs, and other NSX components are connected and configured in your network.
Display how the different NSX components are interconnected: You can use Network Topology to view how your segments, gateways, routers, firewalls, load balancers, VPNs, and other NSX components are connected and configured in your network. Display the uplink configured on the Tier-0 Gateways: You can use Network Topology to view the uplink interface and segment that connect your tier-0 gateways to your physical network. You can also view the VLAN ID and IP address of the uplink interface.
Display the uplink configured on the Tier-0 Gateways: You can use Network Topology to view the uplink interface and segment that connect your tier-0 gateways to your physical network. You can also view the VLAN ID and IP address of the uplink interface. Display the VMs connected to Segments: You can use Network Topology to view the VMs that are attached to your segments. You can also view the IP address and MAC address of each VM.
Display the VMs connected to Segments: You can use Network Topology to view the VMs that are attached to your segments. You can also view the IP address and MAC address of each VM.
NEW QUESTION 8
Which CLI command is used for packet capture on the ESXi Node?
- A. tcpdump
- B. debug
- C. pktcap-uw
- D. set capture
Answer: C
Explanation:
According to the VMware Knowledge Base, this CLI command is used for packet capture on the ESXi node. pktcap-uw stands for Packet Capture User World and is a tool that allows you to capture packets from various points in the network stack of an ESXi host. You can use this tool to troubleshoot network issues or analyze traffic flows.
The other options are either incorrect or not available for this task. tcpdump is not a valid CLI command for packet capture on the ESXi node, as it is a tool that runs on Linux systems, not on ESXi hosts. debug is not a valid CLI command for packet capture on the ESXi node, as it is a generic term that describes the process of finding and fixing errors, not a specific tool or command. set capture is not a valid CLI command for packet capture on the ESXi node, as it does not exist in the ESXi CLI.
NEW QUESTION 9
Refer to the exhibits.
Drag and drop the NSX graphic element icons on the left found in an NSX Intelligence visualization graph to Its correct description on the right.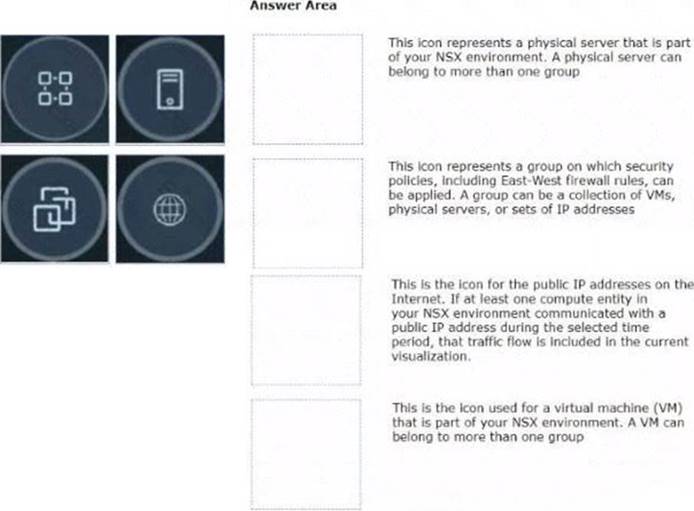
Solution:
https://docs.vmware.com/en/VMware-NSX-Intelligence/4.0/user-guide/GUID-DC78552B-2CC4-410D-A6C9-3
Does this meet the goal?
- A. Yes
- B. Not Mastered
Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 10
Which NSX CLI command is used to change the authentication policy for local users?
- A. Set cli-timeout
- B. Get auth-policy minimum-password-length
- C. Set hardening- policy
- D. Set auth-policy
Answer: D
Explanation:
According to the VMware NSX Documentation4, the set auth-policy command is used to change the authentication policy settings for local users, such as password length, lockout period, and maximum authentication failures. The other commands are either used to view the authentication policy settings (B), change the CLI session timeout (A), or change the hardening policy settings ©.
NEW QUESTION 11
Which two of the following will be used for Ingress traffic on the Edge node supporting a Single Tier topology? (Choose two.)
- A. Inter-Tier interface on the Tier-0 gateway
- B. Tier-0 Uplink interface
- C. Downlink Interface for the Tier-0 DR
- D. Tier-1 SR Router Port
- E. Downlink Interface for the Tier-1 DR
Answer: BC
Explanation:
The two interfaces that will be used for ingress traffic on the Edge node supporting a Single Tier topology are: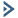 B. Tier-0 Uplink interface
B. Tier-0 Uplink interface C. Downlink Interface for the Tier-0 DR
C. Downlink Interface for the Tier-0 DR
The Tier-0 Uplink interface is the interface that connects the Tier-0 gateway to the external network. It is used to receive traffic from the physical router or switch that is the next hop for the Tier-0 gateway. The Tier-0 Uplink interface can be configured with a static IP address or use BGP to exchange routes with the external network.
The Downlink Interface for the Tier-0 DR is the interface that connects the Tier-0 gateway to the workload segments. It is used to receive traffic from the VMs or containers that are attached to the segments. The Downlink Interface for the Tier-0 DR is a logical interface (LIF) that is distributed across all transport nodes that host the segments. The Downlink Interface for the Tier-0 DR has an IP address that acts as the default gateway for the VMs or containers on the segments.
NEW QUESTION 12
An NSX administrator is using ping to check connectivity between VM1 running on ESXi1 to VM2 running on ESXi2. The ping tests fails. The administrator knows the maximum transmission unit size on the physical switch is 1600.
Which command does the administrator use to check the VMware kernel ports for tunnel end point communication?
- A. esxcli network diag ping -I vmk0O -H <destination IP address>
- B. vmkping ++netstack=geneve -d -s 1572 <destination IP address>
- C. esxcli network diag ping -H <destination IP address>
- D. vmkping ++netstack=vxlan -d -s 1572 <destination IP address>
Answer: B
Explanation:
The command vmkping ++netstack=geneve -d -s 1572 <destination IP address> is used to check the VMwar kernel ports for tunnel end point communication. This command uses the geneve netstack, which is the default netstack for NSX-T. The -d option sets the DF (Don’t Fragment) bit in the IP header, which prevents the packet from being fragmented by intermediate routers. The -s 1572 option sets the packet size to 1572 bytes, which is the maximum payload size for a geneve encapsulated packet with an MTU of 1600 bytes.
The <destination IP address> is the IP address of the remote ESXi host or VM. References: : VMware NS Data Center Installation Guide, page 19. : VMware Knowledge Base: Testing MTU with the vmkping command (1003728). : VMware NSX-T Data Center Administration Guide, page 102.
NEW QUESTION 13
Refer to the exhibit.
An administrator configured NSX Advanced Load Balancer to load balance the production web server traffic, but the end users are unable to access the production website by using the VIP address.
Which of the following Tier-1 gateway route advertisement settings needs to be enabled to resolve the problem? Mark the correct answer by clicking on the image.
Solution:
The correct answer is to enable the option All LB VIP Routes on the Tier-1 gateway route advertisement settings. This option allows the Tier-1 gateway to advertise the NSX Advanced Load Balancer LB VIP routes to the Tier-0 gateway and other peer routers, so that the end users can reach the production website by using the VIP address1. The other options are not relevant for this scenario.
To mark the correct answer by clicking on the image, you can click on the toggle switch next to All LB VIP Routes to turn it on. The switch should change from gray to blue, indicating that the option is enabled. See the image below for reference:
Does this meet the goal?
- A. Yes
- B. Not Mastered
Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 14
What must be configured on Transport Nodes for encapsulation and decapsulation of Geneve protocol?
- A. VXIAN
- B. UDP
- C. STT
- D. TEP
Answer: D
Explanation:
According to the VMware NSX Documentation, TEP stands for Tunnel End Point and is a logical interface that must be configured on transport nodes for encapsulation and decapsulation of Geneve protocol. Geneve is a tunneling protocol that encapsulates the original packet with an outer header that contains metadata such as the virtual network identifier (VNI) and the transport node IP address. TEPs are responsible for adding and removing the Geneve header as the packet traverses the overlay network.
NEW QUESTION 15
Which two are supported by L2 VPN clients? (Choose two.)
- A. NSX for vSphere Edge
- B. 3rd party Hardware VPN Device
- C. NSX Autonomous Edge
- D. NSX Edge
Answer: AD
Explanation:
L2 VPN clients are supported by NSX for vSphere Edge and NSX Edge. NSX for vSphere Edge is a virtual
appliance that provides network services such as routing, firewalling, load balancing, VPN, and NAT for NSX Data Center for vSphere environments. NSX Edge is a virtual appliance that provides network services such as routing, firewalling, load balancing, VPN, and NAT for NSX-T Data Center environments. Both NSX for vSphere Edge and NSX Edge can act as L2 VPN clients to extend layer 2 networks across multiple sites using L2 VPN service over SSL or IPSec tunnels
NEW QUESTION 16
As part of an organization's IT security compliance requirement, NSX Manager must be configured for 2FA (two-factor authentication).
What should an NSX administrator have ready before the integration can be configured? O
- A. Active Directory LDAP integration with OAuth Client added
- B. VMware Identity Manager with an OAuth Client added
- C. Active Directory LDAP integration with ADFS
- D. VMware Identity Manager with NSX added as a Web Application
Answer: B
Explanation:
To configure NSX Manager for two-factor authentication (2FA), an NSX administrator must have VMware
Identity Manager (vIDM) with an OAuth Client added. vIDM provides identity management services and supports various 2FA methods, such as VMware Verify, RSA SecurID, and RADIUS. An OAuth Client is a configuration entity in vIDM that represents an application that can use vIDM for authentication and authorization. NSX Manager must be registered as an OAuth Client in vIDM before it can use
2FA. References: : VMware NSX-T Data Center Installation Guide, page 19. : VMware NSX-T Data Center Administration Guide, page 102. : VMware Blogs: Two-Factor Authentication with VMware NSX-T
NEW QUESTION 17
Which choice is a valid insertion point for North-South network introspection?
- A. Guest VM vNIC
- B. Partner SVM
- C. Tier-0 gateway
- D. Host Physical NIC
Answer: C
Explanation:
A valid insertion point for North-South network introspection is Tier-0 gateway. North-South network introspection is a service insertion feature that allows third-party network services to be integrated with
NSX. North-South network introspection enables traffic redirection from the uplink of an NSX Edge node to a service chain that consists of one or more service profiles1. The Tier-0 gateway is the logical router that connects the NSX Edge node to the physical network and provides North-South routing and network
services2.
https://docs.vmware.com/en/VMware-NSX/4.1/administration/GUID-D5933474-34A2-4DCE-AE9B-A82FF33
NEW QUESTION 18
......
Recommend!! Get the Full 2V0-41.23 dumps in VCE and PDF From Dumps-files.com, Welcome to Download: https://www.dumps-files.com/files/2V0-41.23/ (New 106 Q&As Version)