Exam Code: 300-410 (Practice Exam Latest Test Questions VCE PDF)
Exam Name: Implementing Cisco Enterprise Advanced Routing and Services (ENARSI)
Certification Provider: Cisco
Free Today! Guaranteed Training- Pass 300-410 Exam.
Cisco 300-410 Free Dumps Questions Online, Read and Test Now.
NEW QUESTION 1
A network administrator successfully established a DMVPN tunnel with one hub and two spokes using EIGRP. One of the requirements was to enable spoke-to-spoke tunnels through the hub router using EIGRP. Which configuration command must the engineer configure to meet the requirement?
- A. no ip eigrp 1 mode multipoint
- B. no ip eigrp 1 split-horizon
- C. no ip eigrp 1 tunnel-redirect
- D. no ip eigrp 1 mode mgre
Answer: B
NEW QUESTION 2
Refer to the exhibit.
R1 has a route map configured, which results in a loss of partial IPv6 prefixes for the BGP neighbor, resulting in service degradation. How can the full service be restored?
- A. The neighbor requires a soft reconfiguration, and this will clear the policy without resetting the BGP TCP connection.
- B. The prefix lit requires all prefixes that R1 is advertising to be added to it, and this will allow additional prefixes to be advertised.
- C. The route map requires a deny 20 statement without set conditions, and this will allow additional prefixes to be advertised.
- D. The route map requires a permit 20 statement without set conditions, and this will allow additional prefixes to be advertised.
Answer: D
NEW QUESTION 3
What is a role of route distinguishers in an MPLS network?
- A. Route distinguishers define which prefixes are imported and exported on the edge router
- B. Route distinguishers allow multiple instances of a routing table to coexist within the edge router.
- C. Route distinguishers are used for label bindings.
- D. Route distinguishers make a unique VPNv4 address across the MPLS network
Answer: D
NEW QUESTION 4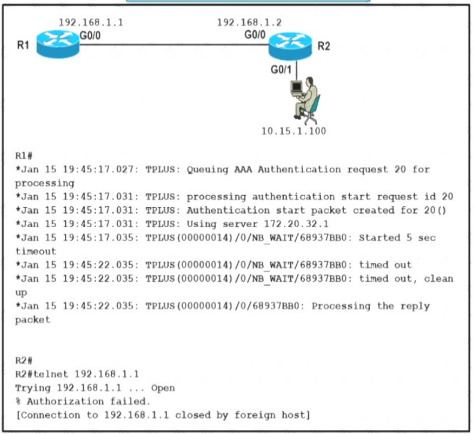
Refer to the exhibit A network engineer is troubleshooting an AAA authentication issue for R1 from R2 When an engineer tries to open a telnet connection to R1 it opens the connection but shows a %Authorization failed error message on the terminal and closes the connection silently Which action resolves the issue?
- A. Resolve tacacs+ server host IP authentication miss configuration on the R1 router
- B. Resolve tacacs+ server reachability from the R1 router.
- C. Configure the tacacs+ server host IP on the R1 router
- D. Configure authorization commands in the tacacs* server for the R1 router.
Answer: D
NEW QUESTION 5
Refer to the exhibit.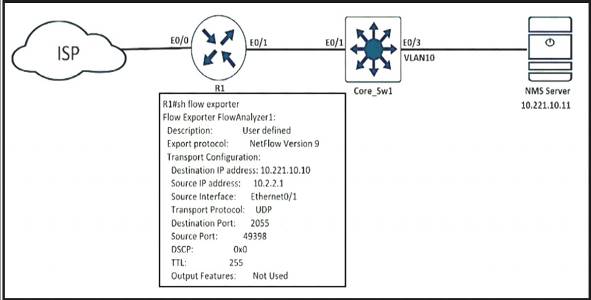
An engineer configured NetFlow on R1, but the NMS server cannot see the flow from R1. Which configuration resolves the issue?
- A. flow monitor Flowmonitor1 destination 10.221.10.11
- B. flow exporter FlowAnalyzer1 destination 10.221.10.11
- C. interface Ethernet0/1flow-destination 10.221.10.11
- D. interface Ethernet0/0flow-destination 10.221.10.11
Answer: B
Explanation:
From the output we notice that the destination IP address is not correct. The NMS server IP address should be 10.221.10.11, not 10.221.10.10. Therefore we have to change this information under “flow exporter …” configuration.
NetFlow configuration reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/iosxml/ ios/fnetflow/configuration/15-mt/fnf-15-mt-book/cfg-de-fnflow-exprts.html
NEW QUESTION 6
Refer to the exhibit.
R1 is connected with R2 via GigabitEthernet0/0, and R2 cannot ping R1. What action will fix the issue?
- A. Fix route dampening configured on the router.
- B. Replace the SFP module because it is not supported.
- C. Fix IP Event Dampening configured on the interface.
- D. Correct the IP SLA probe that failed.
Answer: C
Explanation: 
NEW QUESTION 7
In a DMVPN network, the Spoke1 user observed that the voice traffic is coming to Spoke2 users via the hub router. Which command is required on both spoke routers to communicate directly to one another?
- A. ip nhrp map dynamic
- B. ip nhrp shortcut
- C. ip nhrp nhs multicast
- D. ip nhrp redirect
Answer: B
NEW QUESTION 8
Which rouler takes an active role between two LDP neighbors when initiating LDP session negotiation and LDP TCP connection establishment?
- A. with the higher IP address
- B. with the larger number of LDP TCP neighbors
- C. with the lowest IP address
- D. with one interface in the MPLS backbone
Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 9
Which IPv6 first hop security feature controls the traffic necessary for proper discovery of neighbor device operation and performance?
- A. RA Throttling
- B. Source or Destination Guard
- C. ND Multicast Suppression
- D. IPv6 Snooping
Answer: D
NEW QUESTION 10
Refer to the following output:
Router#show ip nhrp detail 10.1.1.2 /8 via 10.2.1.2, Tunnel1 created 00:00:12, expire 01:59:47 TypE. dynamic, Flags: authoritative unique nat registered used NBMA address: 10.12.1.2
What does the authoritative flag mean in regards to the NHRP information?
- A. It was obtained directly from the next-hop server.
- B. Data packets are process switches for this mapping entry.
- C. NHRP mapping is for networks that are local to this router.
- D. The mapping entry was created in response to an NHRP registration request.
- E. The NHRP mapping entry cannot be overwritten.
Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 11
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator configured an IPv6 access list to allow TCP return traffic only, but it is not working as expected. Which changes resolve this issue?
- A. ipv6 access-list inbound permit tcp any any syn deny ipv6 any any log!interface gi0/0ipv6 traffic-filter inbound out
- B. ipv6 access-list inbound permit tcp any any syn deny ipv6 any any log!interface gi0/0ipv6 traffic-filter inbound in
- C. ipv6 access-list inbound permit tcp any any established deny ipv6 any any log!interface gi0/0ipv6 traffic-filter inbound in
- D. ipv6 access-list inbound permit tcp any any established deny ipv6 any any log!interface gi0/0ipv6 traffic-filter inbound out
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 12
A network administrator is tasked to permit http and https traffic only toward the internet from the User1 laptop to adhere to company’s security policy. The administrator can still ping to www.cisco.com Which interface should the access list 101 be applied to resolve this issue?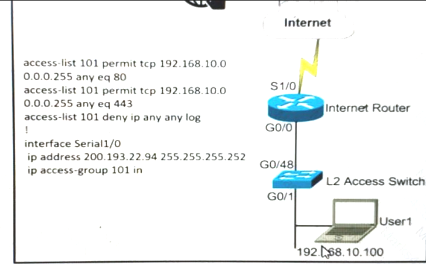
- A. Interface G0/48 in the incoming direction
- B. Interface G0/0 in the outgoing direction.
- C. Interface S1/0 in the outgoing direction.
- D. Interface G0/0 in the incoming direction.
Answer: D
NEW QUESTION 13
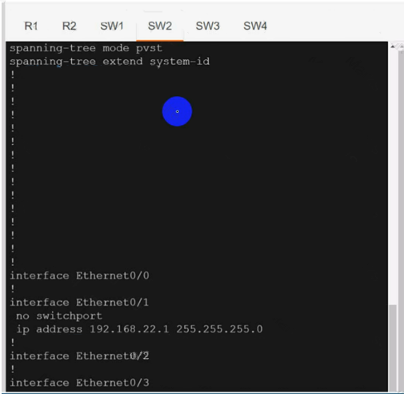
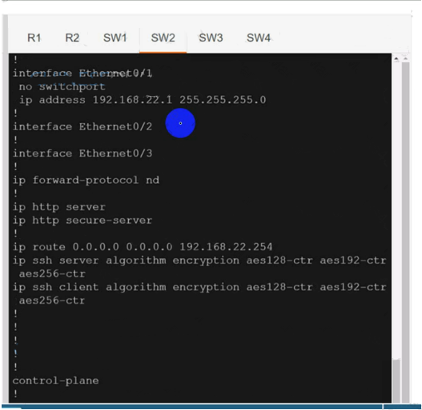
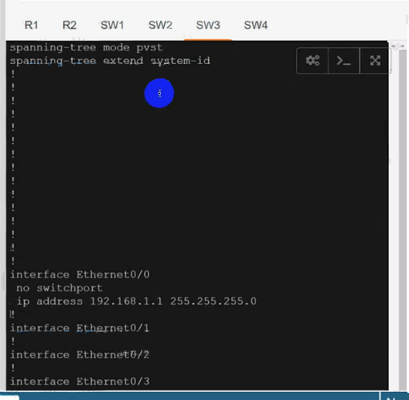
Configure individual VRFs for each customer according to the topology to achieve these goals :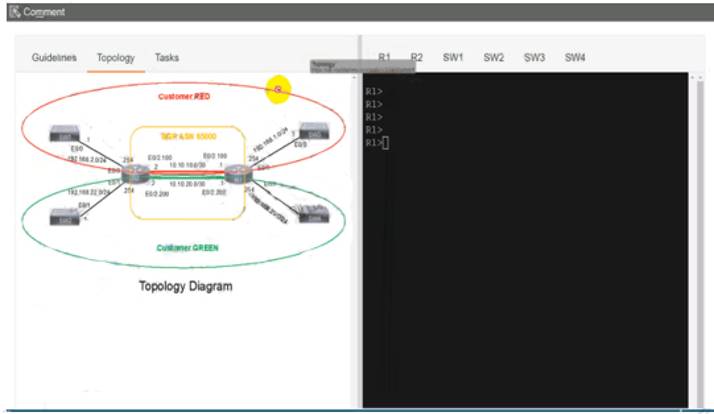

R1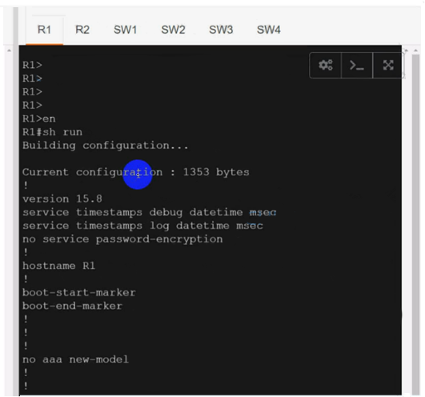
R2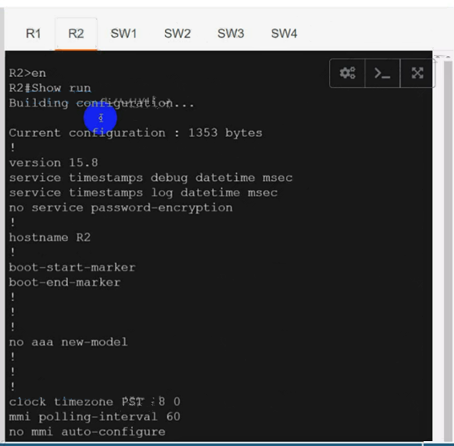

SW1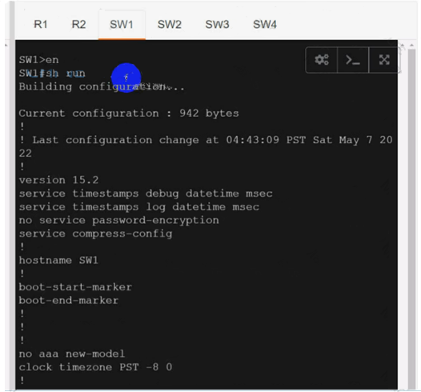
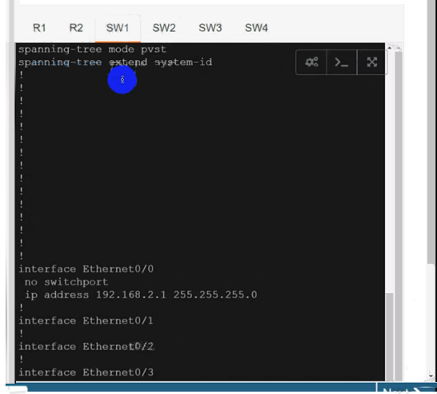
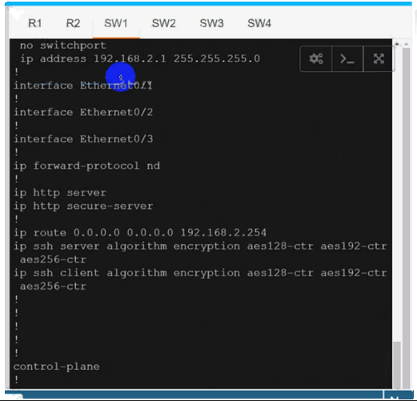
SW2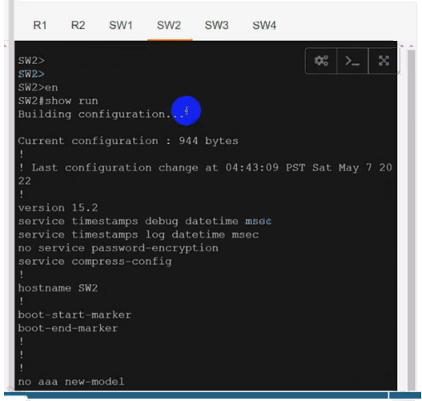
SW3
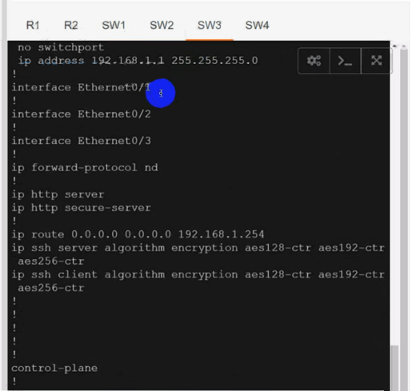
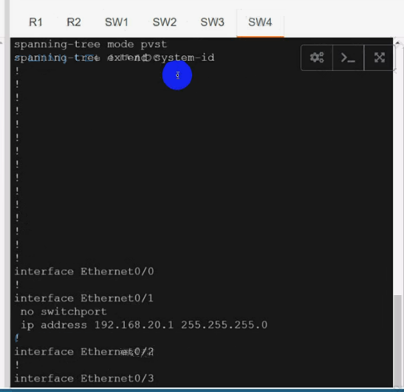
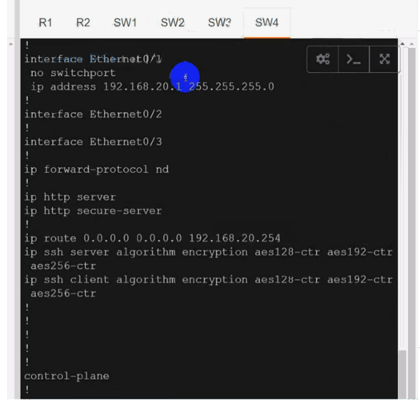
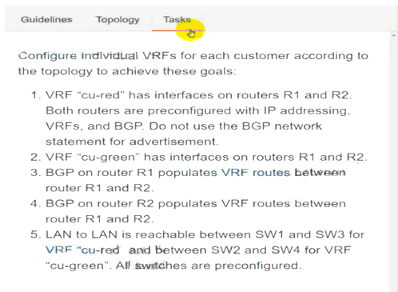
Solution:
Solution:
 Use cu-red under interfaces facing SW1 & SW3:
Use cu-red under interfaces facing SW1 & SW3:On R1:
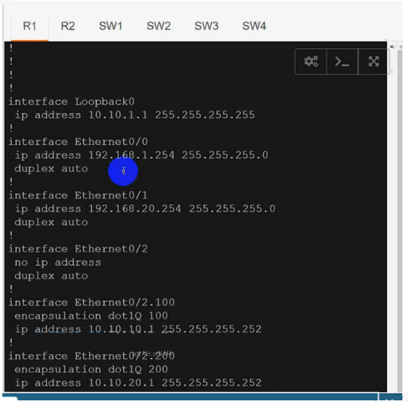
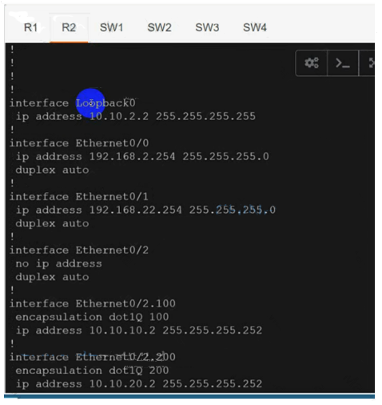
interface Ethernet0/0
ip vrf forwarding cu-red
ip address 192.168.1.254 255.255.255.0
Check reachability to SW1: R1#ping vrf cu-red 192.168.1.1 Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.2.1, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/1/1 ms
On R2:
interface Ethernet0/0
ip vrf forwarding cu-red
ip address 192.168.2.254 255.255.255.0
Check reachability to SW3: R2#ping vrf cu-red 192.168.2.1 Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.1.1, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
 Use vrf cu-green for SW2 & SW4:
Use vrf cu-green for SW2 & SW4:On R1:
interface Ethernet0/1
ip vrf forwarding cu-green
ip address 192.168.20.254 255.255.255.0
Test reachability to SW2: R1#ping vrf cu-green 192.168.20.1 Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.22.1, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/1/1 ms
On R2:
interface Ethernet0/1
ip vrf forwarding cu-green
ip address 192.168.22.254 255.255.255.0
Test reachability to SW4: R2#ping vrf cu-green 192.168.22.1 Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.20.1, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/1/1 ms
 On R1:
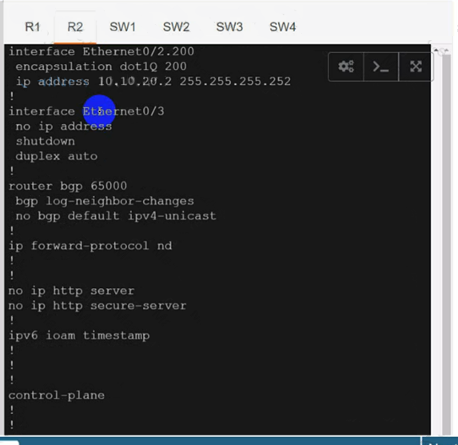
On R1:interface Ethernet0/2.100 mpls ip
!
interface Ethernet0/2.200 mpls ip
!
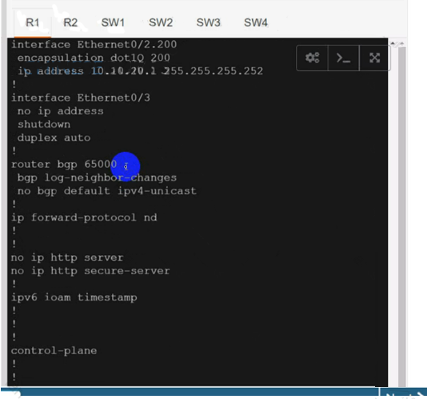
Configure BGP:
router bgp 65000
neighbor 10.10.10.2 remote-as 65000
neighbor 10.10.20.2 remote-as 65000
!
address-family vpnv4 neighbor 10.10.10.2 activate
neighbor 10.10.20.2 activate exit-address-family
!
address-family ipv4 vrf cu-green redistribute connected
exit-address-family
!
address-family ipv4 vrf cu-red redistribute connected
exit-address-family
!
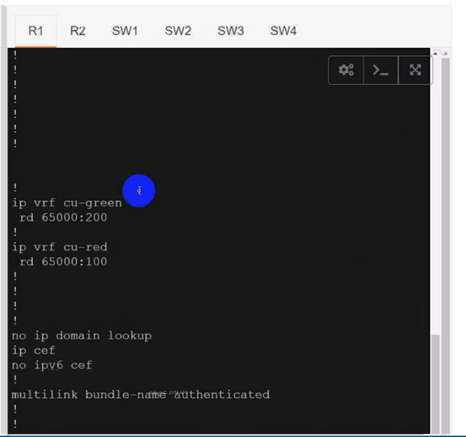
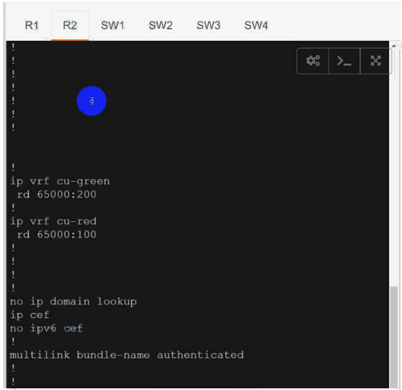
R1(config)#ip vrf cu-red
R1(config-vrf)#route-target both 65000:100
!
R1(config)#ip vrf cu-green
R1(config-vrf)#route-target both 65000:200
 On R2:
On R2:interface Ethernet0/2.100
mpls ip
!
interface Ethernet0/2.200 mpls ip
!
router bgp 65000
neighbor 10.10.10.1 remote-as 65000
neighbor 10.10.20.1 remote-as 65000
!
address-family vpnv4 neighbor 10.10.10.1 activate
neighbor 10.10.20.1 activate exit-address-family
!
address-family ipv4 vrf cu-green redistribute connected
exit-address-family
!
address-family ipv4 vrf cu-red redistribute connected
exit-address-family R2(config)#ip vrf cu-red
R2(config-vrf)#route-target both 65000:100
!
R2(config)#ip vrf cu-green
R2(config-vrf)#route-target both 65000:200
 Verification:
Verification:From SW1 to SW3: SW1#ping 192.168.1.1
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.1.1, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/1/1 ms
But can’t Reach SW2 or SW4 in VRF cu-green: SW1#ping 192.168.22.1
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.22.1, timeout is 2 seconds: U.U.U
Success rate is 0 percent (0/5)
SW1#ping 192.168.20.1
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.20.1, timeout is 2 seconds: U.U.U
Success rate is 0 percent (0/5)
Same Test for SW2: From SW2 to SW4: SW2#ping 192.168.20.1
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.20.1, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/1/1 ms
But can’t Reach SW3 or SW1 in VRF cu-red: SW2#ping 192.168.1.1
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.1.1, timeout is 2 seconds: U.U.U
Success rate is 0 percent (0/5)
SW2#ping 192.168.2.1
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.2.1, timeout is 2 seconds: U.U.U
Success rate is 0 percent (0/5)
Both R1 & R2 has separate tables for VRFs cu-red and cu-green.
Does this meet the goal?
- A. Yes
- B. Not Mastered
Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 14
Which two solutions are used to overcome a flapping link that causes a frequent label binding exchange between MPLS routers? (Choose two)
- A. Create link dampening on links to protect the session.
- B. Increase input queue on links to protect the session.
- C. Create targeted hellos to protect the session.
- D. Increase a hold-timer to protect the session.
- E. Increase a session delay to protect the session.
Answer: AC
Explanation:
To avoid having to rebuild the LDP session altogether, you can protect it. When the LDP session between two directly connected LSRs is protected, a targeted LDP session is built between the two LSRs. When the directly connected link does go down between the two LSRs, the targeted LDP session is kept up as long as an alternative path exists between the two LSRs.
For the protection to work, you need to enable it on both the LSRs. If this is not possible, you can enable it on one LSR, and the other LSR can accept the targeted LDP Hellos by configuring the command mpls ldp discovery targeted-hello accept.
Reference: https://www.ccexpert.us/mpls-network/mpls-ldp-session-protection.html Or from the reference
at https://www.ciscolive.com/c/dam/r/ciscolive/us/docs/2019/pdf/5eU6DfQV/TECMPL-3201.pdf
Troubleshooting LDP Issues
Problem:
I. When a link flaps (for a short time),
… Solution:
+ When LDP session supported by link hello is setup, create a targeted hello to protect the session.
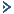
NEW QUESTION 15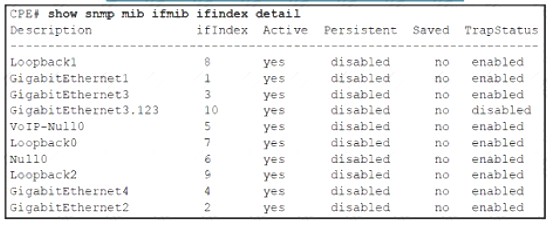
Refer to the exhibit. After reloading the router an administrator discovered that the interface utilization graphs displayed inconsistencies with their previous history in the NMS. Which action prevents this issue from occurring after another router reload in the future?
- A. Rediscover all the router interfaces through SNMP after the router is reloaded
- B. Save the router configuration to startup-config before reloading the router
- C. Configure SNMP to use static OlDs referring to individual router interfaces
- D. Configure SNMP interface index persistence on the router
Answer: D
NEW QUESTION 16
Refer to the exhibit.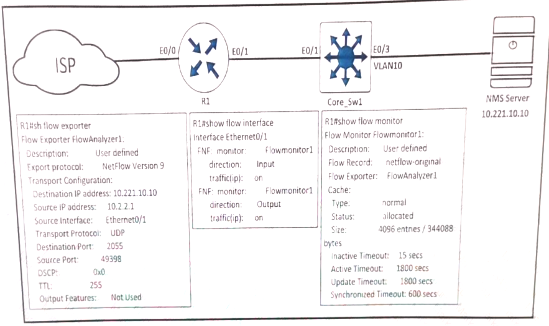
An engineer configured NetFlow on R1, but the NMS server cannot see the flow from ethernet 0/0 of R1. Which configuration resolves the issue?
- A. flow monitor Flowmonitor1 source Ethernet0/0
- B. interface Ethernet0/1ip flow monitor Flowmonitor1 input ip flow monitor Flowmonitor1 output
- C. interface Ethernet0/0ip flow monitor Flowmonitor1 input ip flow monitor Flowmonitor1 output
- D. flow exporter FlowAnalyzer1 source Ethernet0/0
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 17
R1 and R2 are configured as eBGP neighbor , R1 is in AS100 and R2 is in AS200. R2 is advertising these networks to R1:
The network administrator on R1 must improve convergence by blocking all subnets of 172-16.0.0/16 major network with a mask lower than 23 from coming in, Which set of configurations accomplishes the task on R1?
- A. ip prefix-list PL-1 deny 172.16.0.0/16 le 23 ip prefix-list PL-1 permit 0.0.0.0/0 le 32!router bgp 100neighbor 192.168.100.2 remote-as 200 neighbor 192.168.100.2 prefix-list PL-1 in
- B. ip prefix-list PL-1 deny 172.16.0.0/16 ge 23 ip prefix-list PL-1 permit 0.0.0.0/0 le 32!router bgp 100neighbor 192.168.100.2 remote-as 200 neighbor 192.168.100.2 prefix-list PL-1 in
- C. access-list 1 deny 172.16.0.0 0.0.254.255 access-list 1 permit any!router bgp 100neighbor 192.168.100.2 remote-as 200neighbor 192.168.100.2 distribute-list 1 in
- D. ip prefix-list PL-1 deny 172.16.0.0/16 ip prefix-list PL-1 permit 0.0.0.0/0!router bgp 100neighbor 192.168.100.2 remote-as 200 neighbor 192.168.100.2 prefix-list PL-1 in
Answer: A
Explanation:
“Blocking all subnets of 172.16.0.0/16 major network with a mask lower than 23 from coming in” would block 172.16.16.0/20.
The first prefix-list “ip prefix-list PL-1 deny 172.16.0.0/16 le 23” means “all networks that fall within the 172.16.0.0/16 range AND that have a subnet mask of /23 or less” are denied.
The second prefix-list “ip prefix-list PL-1 permit 0.0.0.0/0 le 32” means allows all other prefixes.
NEW QUESTION 18
Refer to the exhibit.
When monitoring an IPv6 access list, an engineer notices that the ACL does not have any hits and is causing unnecessary traffic to pass through the interface Which command must be configured to resolve the issue?
- A. access-class INTERNET in
- B. ipv6 traffic-filter INTERNET in
- C. ipv6 access-class INTERNET in
- D. ip access-group INTERNET in
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 19
Refer to the exhibit.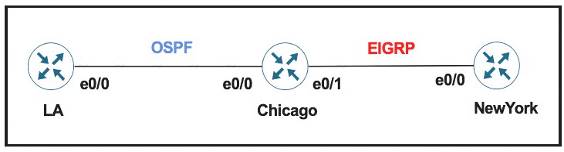
The network administrator must mutually redistribute routes at the Chicago router to the LA and NewYork routers. The configuration of the Chicago router is this:
After the configuration, the LA router receives all the NewYork routes, but NewYork router does not receive any LA routes. Which set of configurations fixes the problem on the Chicago router?
A)
B)
C)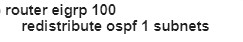
D)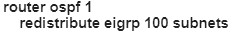
- A. Option A
- B. Option B
- C. Option C
- D. Option D
Answer: B
Explanation:
“LA router receives all the NewYork routes but it does not receive any LA routes” because when redistrubuting into EIGRP, we must configure the default metric.
NEW QUESTION 20
A network administrator performed a Compact Flash Memory upgrade on a Cisco Catalyst 6509 Switch. Everything is functioning normally except SNMP, which was configured to monitor the bandwidth of key interfaces but the interface indexes are changed. Which global configuration resolves the issue?
- A. snmp-server ifindex permanent
- B. snmp ifindex permanent
- C. snmp-server ifindex persist
- D. snmp ifindex persist
Answer: C
Explanation:
The SNMP ifIndex persistence feature provides an interface index (ifIndex) value that is retained and used when the router reboots. The ifIndex value is a unique identifying number associated with a physical or logical interface. In the following example, SNMP ifIndex persistence is enabled for all interfaces:
router(config)# snmp-server ifindex persist
NEW QUESTION 21
......
Recommend!! Get the Full 300-410 dumps in VCE and PDF From Certshared, Welcome to Download: https://www.certshared.com/exam/300-410/ (New 575 Q&As Version)