are updated and are verified by experts. Once you have completely prepared with our you will be ready for the real 200-101 exam without a problem. We have . PASSED First attempt! Here What I Did.
Online 200-101 free questions and answers of New Version:
NEW QUESTION 1
What is the default administrative distance of OSPF?
- A. 90
- B. 100
- C. 110
- D. 120
Answer: C
Explanation: Default Distance Value Table
This table lists the administrative distance default values of the protocols that Cisco supports: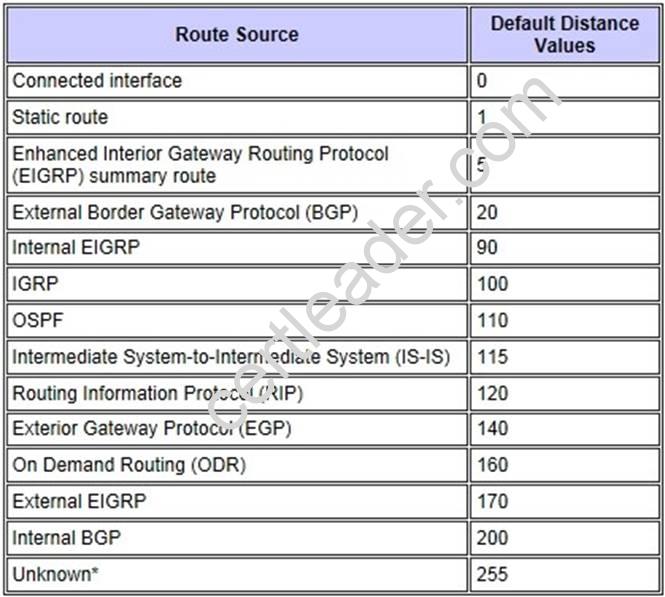
NEW QUESTION 2
CORRECT TEXT
A sporting goods manufacturer has decided to network three (3) locations to improve efficiency in inventory control. The routers have been named to reflect the location: Boston, Frankfurt, and Lancaster.
The necessary networking has been completed at each location, and the routers have been configured with single area OSPF as the routing protocol. The Boston router was recently installed but connectivity is not complete because of incomplete routing tables. Identify and correct any problem you see in the configuration.
Note: The OSPF process must be configured to allow interfaces in specific subnets to participate in the routing process.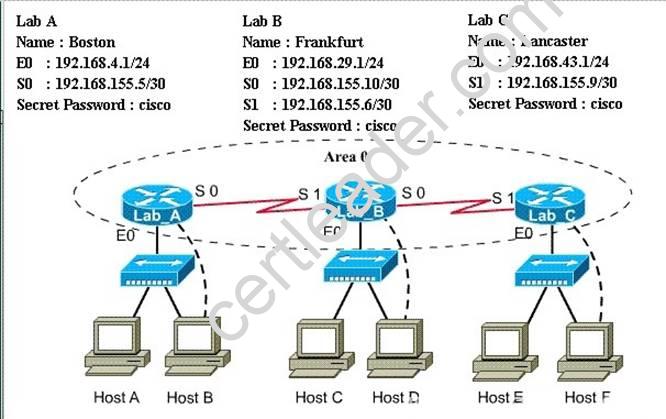
Answer:
Explanation: Boston>enable (type cisco as its password here)
Boston#show running-config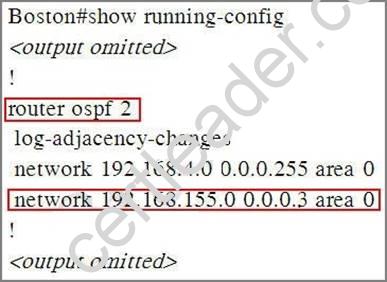
First, remember that the current OSPF Process ID is 2 because we will need it for later configuration. Next notice that in the second “network” command the network and wildcard mask are 192.168.155.0 and 0.0.0.3 which is equivalent to 192.168.155.0 255.255.255.252 in term of subnet mask. Therefore this subnetwork’s range is from 192.168.155.0 to 192.168.155.3 but the ip address of s0/0 interface of Boston router is 192.168.155.5 which don’t belong to this range -> this is the reason why OSPF did not recognize s0 interface of Boston router as a part of area 0. So we need to find a subnetwork that s0 interface belongs to.
IP address of S0 interface: 192.168.155.5/30
Subnet mask: /30 = 1111 1111.1111 1111.1111 1111.1111 1100
Increment: 4
Network address (which IP address of s0 interface belongs to): 192.168.155.4 (because 4 * 1 = 4 < 5)
Therefore we must use this network instead of 192.168.155.0 network
Boston#configure terminal Boston(config)#router ospf 2
Boston(config-router)#no network 192.168.155.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
Boston(config-router)#network 192.168.155.4 0.0.0.3 area 0
Boston(config-router)#end
Boston#copy running-config startup-config
Finally, you should issue a ping command from Boston router to Lancaster router to make sure it works well.
Boston#ping 192.168.43.1
NEW QUESTION 3
Refer to the exhibit.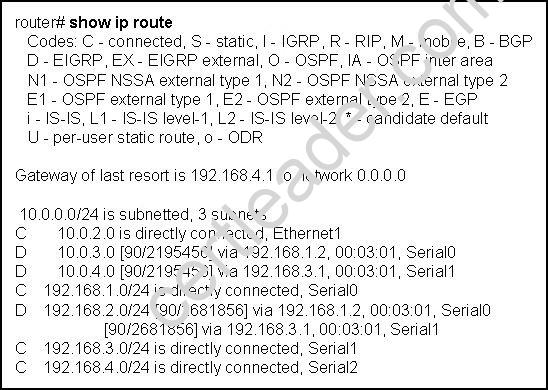
How will the router handle a packet destined for 192.0.2.156?
- A. The router will drop the packet.
- B. The router will return the packet to its source.
- C. The router will forward the packet via Serial2.
- D. The router will forward the packet via either Serial0 or Serial1.
Answer: C
Explanation: Router has pointed default router to 192.168.4.1 and this subnet is connected via serial 2 interface. Router does not have router for the 192.0.2.156. so it will use the default gateway 192.168.4.1. A default route identifies the gateway IP address to which the router sends all IP packets for which it does not have a learned or static route.
NEW QUESTION 4
Refer to the exhibit.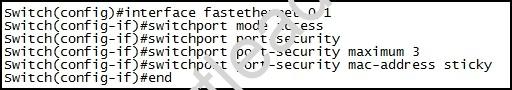
Which of these correctly describes the results of port security violation of an unknown packet?
- A. port enabled; unknown packets dropped; no SNMP or syslog messages
- B. port enabled; unknown packets dropped; SNMP or syslog messages
- C. port disabled; no SNMP or syslog messages
- D. port disabled; SNMP or syslog messages
Answer: D
Explanation: Configuring Port Security
http://packetlife.net/blog/2010/may/3/port-security/
We can view the default port security configuration with show port-security: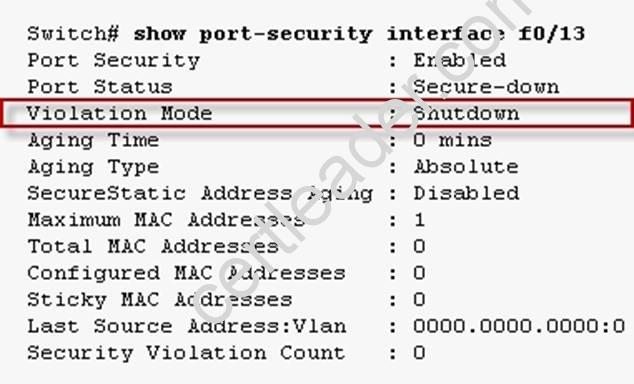
http://www.ciscopress.com/articles/article.asp?p=1722561
Switchport Security Violations
The second piece of switchport port-security that must be understood is a security violation including what it is what causes it and what the different violation modes that exist. A switchport violation occurs in one of two situations:
When the maximum number of secure MAC addresses has been reached (by default, the maximum number of secure MAC addresses per switchport is limited to 1)
An address learned or configured on one secure interface is seen on another secure interface in the same VLAN
The action that the device takes when one of these violations occurs can be configured: Protect—This mode permits traffic from known MAC addresses to continue to be forwarded while dropping traffic from unknown MAC addresses when over the allowed MAC address limit. When configured with this mode, no notification action is taken when traffic is dropped.
Restrict—This mode permits traffic from known MAC addresses to continue to be forwarded while dropping traffic from unknown MAC addresses when over the allowed MAC address limit. When configured with this mode, a syslog message is logged, a Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) trap is sent, and a violation counter is incremented when traffic is dropped.
Shutdown—This mode is the default violation mode; when in this mode, the switch will automatically force the switchport into an error disabled (err-disable) state when a violation
occurs. While in this state, the switchport forwards no traffic. The switchport can be brought out of this error disabled state by issuing the errdisable recovery cause CLI command or by disabling and re-enabling the switchport.
Shutdown VLAN—This mode mimics the behavior of the shutdown mode but limits the error disabled state the specific violating VLAN.
NEW QUESTION 5
DRAG DROP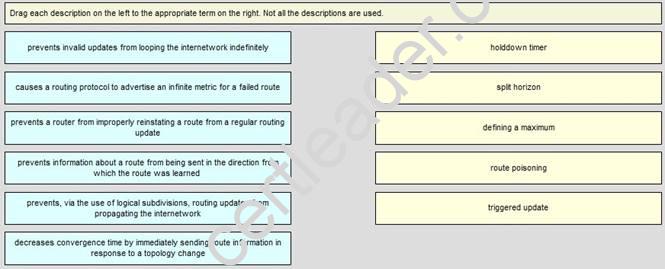
Answer:
Explanation: 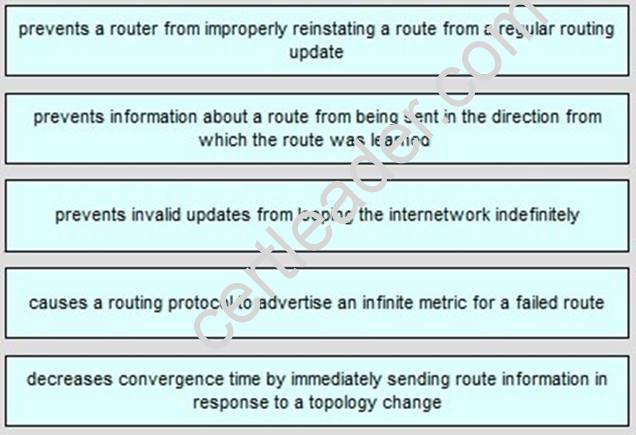
Reference:
http://www.9tut.net/icnd2/icnd2-drag-and-drop-questions-2
+ holddown timer: prevents a router from improperly reinstating a route from a regular routing update
+ split horizon: prevents information about a route from being sent in the direction from which the route was learned
+ defining a maximum: prevents invalid updates from looping the internetwork indefinitely
+ route poisoning: causes a routing protocol to advertise an infinite metric for a failed route
+ triggered update: decreases convergence time by immediately sending route information in response to a topology change
NEW QUESTION 6
CORRECT TEXT
A network associate is configuring a router for the weaver company to provide internet access. The ISP has provided the company six public IP addresses of 198.18.184.105 198.18.184.110. The company has 14 hosts that need to access the internet simultaneously. The hosts in the company LAN have been assigned private space addresses in the range of 192.168.100.17 - 192.168.100.30.

Answer:
Explanation: In this case, you have to consider using NAT Overload (or PAT)
Doubleclick on the Weaver router to access the CLI
Router> enable
Router# configure terminal
First you should change the router's name to Weaver:
Router(config)#hostname Weaver
Create a NAT pool of global addresses to be allocated with their netmask:
Weaver(config)# ip nat pool mypool 198.18.184.105 198.18.184.110 netmask 255.255.255.248
Create a standard access control list that permits the addresses that are to be translated: Weaver(config)#access-list 1 permit 192.168.100.16 0.0.0.15
Establish dynamic source translation, specifying the access list that was defined in the prior step:
Weaver(config)#ip nat inside source list 1 pool mypool overload
Finally, we should save all your work with the following command:
Weaver#copy running-config startup-config (Don't forget this)
Check your configuration by going to "Host for testing" and type:
C : >ping 192.0.2.114
The ping should work well and you will be replied from 192.0.2.114
This command translates all source addresses that pass access list 1, which means a source address from 192.168.100.17 to 192.168.100.30, into an address from the pool named mypool (the pool contains addresses from 198.18.184.105 to 198.18.184.110) Overload keyword allowsto map multiple IP addresses to a single registered IP address (many-to- one) by using different ports.
The question said that appropriate interfaces have been configured for NAT inside and NAT outside statements.
This is how to configure the NAT inside and NAT outside, just for your understanding: Weaver(config)#interface fa0/0
Weaver(config-if)#ip nat inside
Weaver(config-if)#exit
Weaver(config)#interface s0/0
Weaver(config-if)#ip nat outside
Weaver(config-if)#end
NEW QUESTION 7
Refer to the exhibit.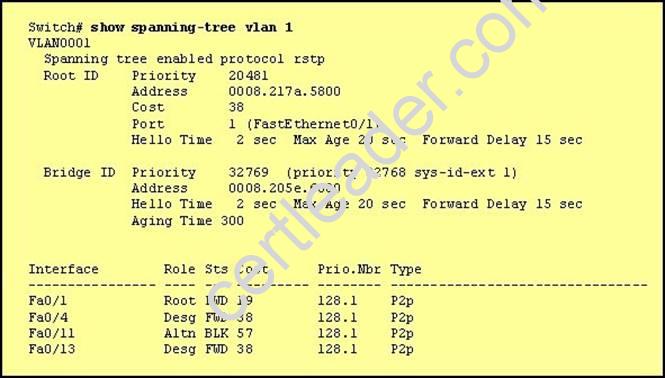
Why has this switch not been elected the root bridge for VLAN1?
- A. It has more than one interface that is connected to the root network segment.
- B. It is running RSTP while the elected root bridge is running 802.1d spanning tree.
- C. It has a higher MAC address than the elected root bridge.
- D. It has a higher bridge ID than the elected root bridge.
Answer: D
Explanation: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk389/tk621/technologies_tech_note09186a008009482f.s html
When a switch receives a BPDU, it first compares priority, the lower number wins. If a tie, compare MAC, the smaller one wins. Here Switch has 32769 priority which is greater than 20481 so switch will not elect for root bridge. It says the bridge priority for Switch is 32769, andthe root priority is 20481. Which means that some other switch has the lower priority and won the election for VLAN 1.
NEW QUESTION 8
What is one benefit of PVST+?
- A. PVST+ supports Layer 3 load balancing without loops.
- B. PVST+ reduces the CPU cycles for all the switches in the network.
- C. PVST+ allows the root switch location to be optimized per VLAN.
- D. PVST+ automatically selects the root bridge location, to provide optimized bandwidth usage.
Answer: C
Explanation: Per VLAN Spanning Tree (PVST)
Introduction http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk389/tk621/tk846/tsd_technology_support_sub-protocol_home.html
Per VLAN Spanning Tree (PVST) maintains a spanning tree instance for each VLAN configured in the network. This means a switch can be the root bridge of a VLAN while another switch can be the root bridge of other VLANs in a common topology. For example, Switch 1 can be the root bridge for Voice data while Switch 2 can be the root bridge for Video data. If designed correctly, it can optimize the network traffic. http://www.ciscopress.com/articles/article.asp?p=102157&seqNum=4
NEW QUESTION 9
Which commands are required to properly configure a router to run OSPF and to add network 192.168.16.0/24 to OSPF area 0? (Choose two.)
- A. Router(config)# router ospf 0
- B. Router(config)# router ospf 1
- C. Router(config)# router ospf area 0
- D. Router(config-router)# network 192.168.16.0 0.0.0.255 0
- E. Router(config-router)# network 192.168.16.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
- F. Router(config-router)# network 192.168.16.0 255.255.255.0 area 0
Answer: BE
Explanation: In the router ospf
Command, theranges from 1 to 65535 so o is an invalid number - B is correct but A is not correct. To configure OSPF, we need a wildcard in the “network” statement, not a subnet mask. We also need to assgin an area to this process - E is correct.
NEW QUESTION 10
At which layer of the OSI model does PPP perform?
- A. Layer 2
- B. Layer 3
- C. Layer 4
- D. Layer 5
Answer: A
Explanation: Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) is adata linkprotocolcommonly used in establishing a direct connection between twonetworking nodes. It can provide connectionauthentication, transmissionencryption(usingECP,RFC 1968), andcompression.
NEW QUESTION 11
Users have been complaining that their Frame Relay connection to the corporate site is very slow. The network administrator suspects that the link is overloaded. Based on the partial output of the Router # show frame relay pvc command shown in the graphic, which output value indicates to the local router that traffic sent to the corporate site is experiencing congestion?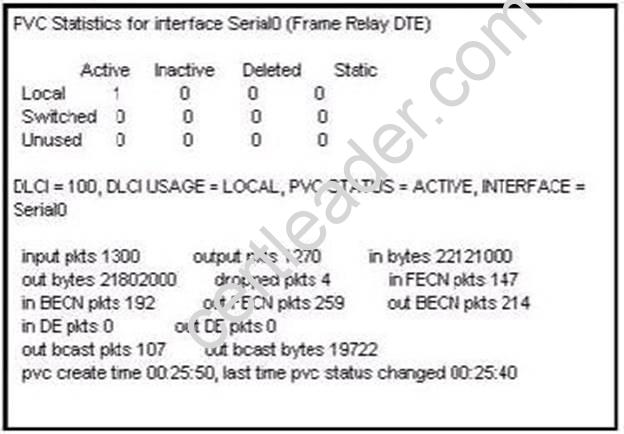
- A. DLCI=100
- B. last time PVC status changed 00:25:40
- C. in BECN packets 192
- D. in FECN packets 147
- E. in DF packets 0
Answer: C
Explanation: First we should grasp the concept of BECN & FECN through an example: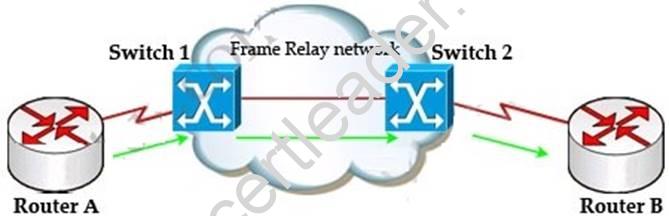
Suppose Router A wants to send data to Router B through a Frame Relay network. If the network is congested, Switch 1 (a DCE device) will set the FECN bit value of that frame to 1, indicating that frame experienced congestion in the path from source to destination. This frame is forwarded to Switch 2 and to Router B (with the FECN bit = 1).
Switch 1 knows that the network is congesting so it also sends frames back to Router A
with BECN bit set to 1 to inform that path through the network is congested.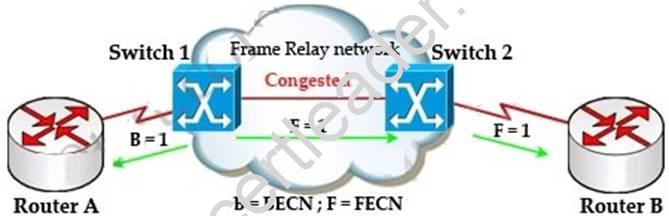
In general, BECN is used on frames traveling away from the congested area to warn source devices that congestion has occurred on that path while FECN is used to alert receiving devices if the frame experiences congestion.
BECN also informs the transmitting devices to slow down the traffic a bit until the network returns to normal state.
The question asks “which output value indicates to the local router that traffic sent to the corporate site is experiencing congestion” which means it asks about the returned parameter which indicates congestion ->BECN.
NEW QUESTION 12
Which three statements about HSRP operation are true? (Choose three.)
- A. The virtual IP address and virtual MA+K44C address are active on the HSRP Master router.
- B. The HSRP default timers are a 3 second hello interval and a 10 second dead interval.
- C. HSRP supports only clear-text authentication.
- D. The HSRP virtual IP address must be on a different subnet than the routers' interfaces on the same LAN.
- E. The HSRP virtual IP address must be the same as one of the router's interface addresses on the LAN.
- F. HSRP supports up to 255 groups per interface, enabling an administrative form of load balancing.
Answer: ABF
NEW QUESTION 13
The network administrator has been asked to give reasons for moving from IPv4 to IPv6. What are two valid reasons for adopting IPv6 over IPv4? (Choose two.)
- A. no broadcast
- B. change of source address in the IPv6 header
- C. change of destination address in the IPv6 header
- D. Telnet access does not require a password
- E. autoconfig
- F. NAT
Answer: AE
Explanation: Six Benefits Of IPv6
http://www.networkcomputing.com/ipv6/six-benefits-of-ipv6/230500009
With IPv6, everything from appliances to automobiles can be interconnected. But an increased number of IT addresses isn't the only advantage of IPv6 over IPv4. In honor of World IPv6 Day, here are six more good reasons to make sure your hardware, software, and services support IPv6.
More Efficient Routing IPv6 reduces the size of routing tables and makes routing more efficient and hierarchical. IPv6 allows ISPs to aggregate the prefixes of their customers' networks into a single prefix and announce this one prefix to the IPv6 Internet. In addition, in IPv6 networks, fragmentation is handled by the source device, rather than the router, using a protocol for discovery of the path's maximum transmission unit (MTU).
More Efficient Packet Processing
IPv6's simplified packet header makes packet processing more efficient. Compared with IPv4, IPv6 contains no IP-level checksum, so the checksum does not need to be recalculated at every router hop. Getting rid of the IPlevel checksum was possible because most link-layer technologies already contain checksum and error-control capabilities. In addition, most transport layers, which handle end-to-end connectivity, have a checksum that enables error detection.
Directed Data Flows IPv6 supports multicast rather than broadcast. Multicast allows bandwidth-intensive packet flows (like multimedia streams) to be sent to multiple destinations simultaneously, saving network bandwidth.
Disinterested hosts no longer must process broadcast packets. In addition, the IPv6 header has a new field, named Flow Label, that can identify packets belonging to the same flow. Simplified Network Configuration Address auto-configuration (address assignment) is built in to IPv6. A router will send the prefix of the local link in its router advertisements. A host can generate its own IP address by appending its link-layer (MAC) address, converted into Extended Universal Identifier (EUI) 64-bit format, to the 64 bits of the local link prefix.
Support For New Services
By eliminating Network Address Translation (NAT), true end-to-end connectivity at the IP layer is restored, enabling new and valuable services. Peer-to-peer networks are easier to create and maintain, and services such as VoIP and Quality of Service (QoS) become more robust.
Security IPSec, which provides confidentiality, authentication and data integrity, is baked into in IPv6. Because of their potential to carry malware, IPv4 ICMP packets are often blocked bycorporate firewalls, but ICMPv6, the implementation of the Internet Control Message Protocol for IPv6, may be permitted because IPSec can be applied to the ICMPv6 packets.
NEW QUESTION 14
When a router undergoes the exchange protocol within OSPF, in what order does it pass through each state?
- A. exstart state > loading state > exchange state > full state
- B. exstart state > exchange state > loading state > full state
- C. exstart state > full state > loading state > exchange state
- D. loading state > exchange state > full state > exstart state
Answer: B
Explanation: Why Are OSPF Neighbors Stuck in Exstart/Exchange State? Reference:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk365/technologies_tech_note09186a0080093f0d.shtml
NEW QUESTION 15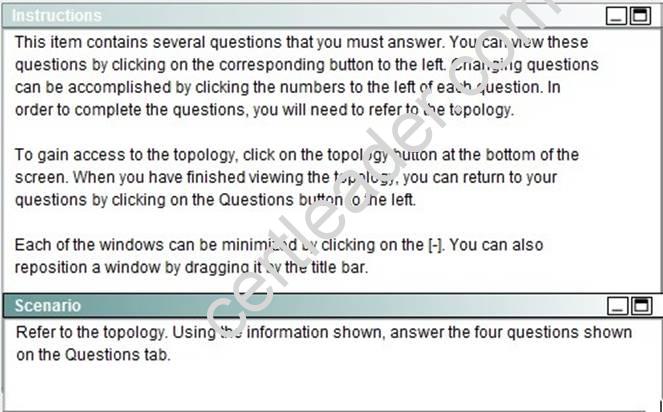
To allow or prevent load balancing to network 172.16.3.0/24, which of the following commands could be used in R2? (Choose two.)
- A. R2(config-if)#clock rate
- B. R2(config-if)#bandwidth
- C. R2(config-if)#ip ospf cost
- D. R2(config-if)#ip ospf priority
- E. R2(config-router)#distance ospf
Answer: BC
Explanation: OSPF Cost
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk365/technologies_white_paper09186a0080094e9e.sht ml#t6
The cost (also called metric) of an interface in OSPF is an indication of the overhead required to send packets across a certain interface. The cost of an interface is inversely proportional to the bandwidth of that interface. A higher bandwidth indicates a lower cost. There is more overhead (higher cost) and time delays involved in crossing a 56k serial line than crossing a 10M ethernet line. The formula used to calculate the cost is:
cost= 10000 0000/bandwith in bps
For example, it will cost 10 EXP8/10 EXP7 = 10 to cross a 10M Ethernet line and will cost 10 EXP8/1544000 =64 to cross a T1 line.
By default, the cost of an interface is calculated based on the bandwidth; you can force the cost of an interface with the ip ospf cost <value> interface subconfiguration mode command.
NEW QUESTION 16
What can be done to Frame Relay to resolve split-horizon issues?(Choose two.)
- A. Disable Inverse ARP.
- B. Create a full-mesh topology.
- C. Develop multipoint subinterfaces.
- D. Configure point-to-point subinterfaces.
- E. Remove the broadcast keyword from the frame-relay map command.
Answer: BD
Explanation: IP split horizon checking is disabled by default for Frame Relay encapsulation to allow routing updates to go in and out of the same interface. An exception is the Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) for which split horizon must be explicitly disabled.
Certain protocols such as AppleTalk, transparent bridging, and Internetwork Packet Exchange (IPX) cannot be supported on partially meshed networks because they require split horizon to be enabled (a packet received on an interface cannot be transmitted over the same interface, even if the packet is received and transmitted on different virtual circuits).
Configuring Frame Relay subinterfaces ensures that a single physical interface is treated as multiple virtual interfaces. This capability allows you to overcome split horizon rules so packets received on one virtual interface can be forwarded to another virtual interface, even if they are configured on the same physical interface.
NEW QUESTION 17
Which two states are the port states when RSTP has converged? (Choose two.)
- A. discarding
- B. listening
- C. learning
- D. forwarding
- E. disabled
Answer: AD
Explanation: Understanding Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (802.1w)
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk389/tk621/technologies_white_paper09186a0080094cf a.shtml
Port States
There are only three port states left in RSTP that correspond to the three possible operational states. The 802.1D disabled, blocking, and listening states are merged into a unique 802.1w discarding state.
RSTP only has 3 port states which are discarding, learning and forwarding. When RSTP has converged there are only 2 port states left: discarding and forwarding.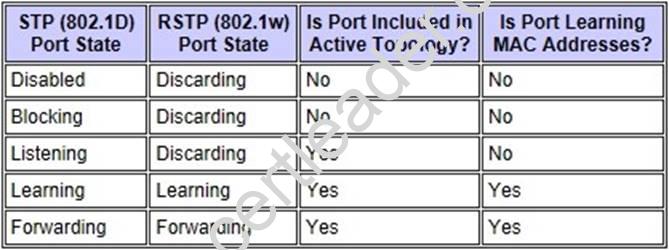
NEW QUESTION 18
Which two statements about the OSPF Router ID are true? (Choose two.)
- A. It identifies the source of a Type 1 LSA.
- B. It should be the same on all routers in an OSPF routing instance.
- C. By default, the lowest IP address on the router becomes the OSPF Router ID.
- D. The router automatically chooses the IP address of a loopback as the OSPF Router ID.
- E. It is created using the MAC Address of the loopback interface.
Answer: AD
NEW QUESTION 19
Refer to the exhibit.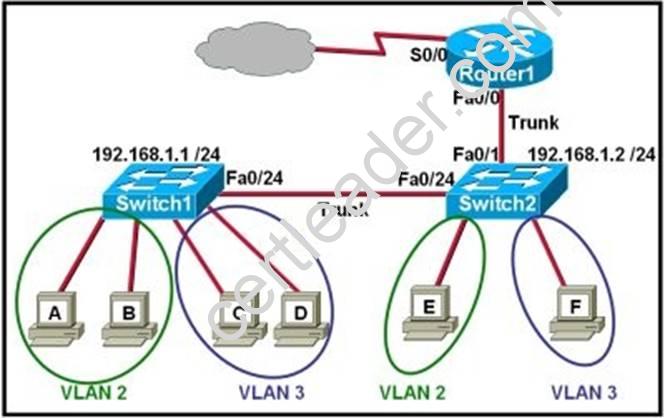
Which two statements are true about interVLAN routing in the topology that is shown in the exhibit? (Choose two.)
- A. Host E and host F use the same IP gateway address.
- B. Router1 and Switch2 should be connected via a crossover cable.
- C. Router1 will not play a role in communications between host A and host D.
- D. The FastEthernet 0/0 interface on Router1 must be configured with subinterfaces.
- E. Router1 needs more LAN interfaces to accommodate the VLANs that are shown in the exhibit.
- F. The FastEthernet 0/0 interface on Router1 and the FastEthernet 0/1 interface on Switch2 trunk ports must be configured using the same encapsulation type.
Answer: DF
Explanation: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk389/tk815/technologies_configuration_example09186a 00800949fd.shtml
100% Valid and Newest Version 200-101 Questions & Answers shared by Surepassexam, Get Full Dumps HERE: https://www.surepassexam.com/200-101-exam-dumps.html (New 149 Q&As)