It is more faster and easier to pass the by using . Immediate access to the and find the same core area with professionally verified answers, then PASS your exam with a high score now.
Also have 200-101 free dumps questions for you:
NEW QUESTION 1
CORRECT TEXT
A new switch is being added to the River Campus LAN. You will work to complete this process by first configuring the building_2 switch with an IP address and default gateway. For the switch host address, you should use the last available IP address on the management subnet. In addition, the switch needs to be configured to be in the same VTP domain as the building_1 switch and also needs to be configured as a VTP client. Assume that the IP configuration and VTP configuration on building_1 are complete and correct. The configuration of the router is not accessible for this exercise. You must accomplish the following tasks:
Determine and configure the IP host address of the new switch. Determine and configure the default gateway of the new switch. Determine and configure the correct VTP domain name for the new switch.
Configure the new switch as a VTP client.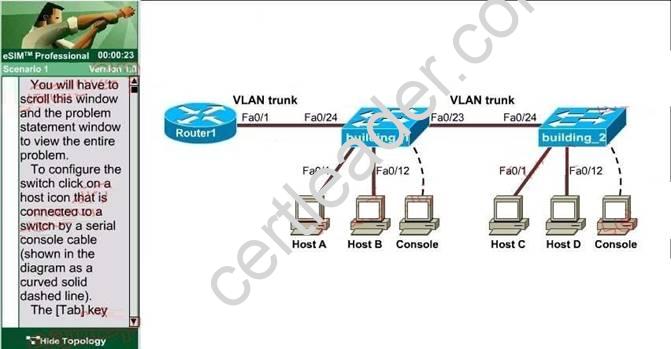
Answer:
Explanation: The question states we can't access the router so we can only get required information from switch building_1. Click on the PC connected with switch building_1 (through a console line) to access switch building_1s CLI. On this switch use the show running-config command:
building_1#show running-config
Next use the show vtp status command to learn about the vtp domain on this switch building_1#show vtp status
(Notice: the IP address, IP default-gateway and VTP domain name might be different!!!) You should write down these 3 parameters carefully.
Configuring the new switch
+ Determine and configure the IP host address of the new switch The question requires "for the switch host address, you should use the last available IP address on the management subnet". The building_1 switch's IP address, which is 192.168.22.50 255.255.255.224, belongs to the management subnet.
Increment: 32 (because 224 = 1110 0000)
Network address: 192.168.22.32
Broadcast address: 192.168.22.63
->The last available IP address on the management subnet is 192.168.22.62 and it hasn't been used (notice that the IP address of Fa0/1 interface of the router is also the default gateway address 192.168.22.35).
Also notice that the management IP address of a switch should be configured in Vlan1 interface. After it is configured, we can connect to it via telnet or SSH to manage it. Switch2#configure terminal
Switch2(config)#interface Vlan1
Switch2(config-if)#ip address 192.168.22.62 255.255.255.224
Switch2(config-if)#no shutdown (not really necessary since VLAN interfaces are not physical and are not shut
down but, no harm in doing so and is good practice for physical ports)
+ Determine and configure the default gateway of the new switch The default gateway of this new switch is same as that of building_1 switch, which is 192.168.22.35 Switch2(config-if)#exit
Switch2(config)#ip default-gateway 192.168.22.35
+ Determine and configure the correct VTP domain name for the new switch The VTP domain name shown on building_1 switch is Cisco so we have to use it in the new switch (notice: the VTP domain name will be different in the exam and it is case sensitive so be careful)
Switch2(config)#vtp domain Cisco
+ Configure the new switch as a VTP client Switch2(config)#vtp mode client
We should check the new configuration with the "show running-config" & "show vtp status"; also try pinging from the new switch to the the default gateway to make sure it works well. Finally save the configuration:
Switch2(config)#exit
Switch2#copy running-config startup-config
NEW QUESTION 2
What are the benefit of using Netflow? (Choose three.)
- A. Network, Application & User Monitoring
- B. Network Planning
- C. Security Analysis
- D. Accounting/Billing
Answer: ACD
Explanation: NetFlow traditionally enables several key customer applications including:
Network Monitoring—NetFlow data enables extensive near real time network monitoring capabilities. Flowbased analysis techniques may be utilized to visualize traffic patterns associated with individual routers and switches as well as on a network-wide basis (providing aggregate traffic or application based views) to provide proactive problem detection, efficient troubleshooting, and rapid problem resolution.
Application Monitoring and Profiling—NetFlow data enables network managers to gain a detailed, timebased, view of application usage over the network. This information is used to plan, understand new services, and allocate network and application resources (e.g. Web server sizing and VoIP deployment) to responsively meet customer demands.
User Monitoring and Profiling—NetFlow data enables network engineers to gain detailed understanding of customer/user utilization of network and application resources. This information may then be utilized to efficiently plan and allocate access, backbone and application resources as well as to detect and resolve potential security and policy violations.
Network Planning—NetFlow can be used to capture data over a long period of time producing the opportunity to track and anticipate network growth and plan upgrades to increase the number of routing devices, ports, or higher- bandwidth interfaces. NetFlow services data optimizes network planning including peering, backbone upgrade planning, and routing policy planning. NetFlow helps to minimize the total cost of network operations while maximizing network performance, capacity, and reliability. NetFlow detects unwanted WAN traffic, validates bandwidth and Quality of Service (QOS) and allows the analysis of new network applications.
NetFlow will give you valuable information to reduce the cost of operating your network. Security Analysis—NetFlow identifies and classifies DDOS attacks, viruses and worms in
real-time. Changes in network behavior indicate anomalies that are clearly demonstrated in NetFlow data. The data is also a valuable forensic tool to understand and replay the history of security incidents.
Accounting/Billing—NetFlow data provides fine-grained metering (e.g. flow data includes details such as IP addresses, packet and byte counts, timestamps, type-of-service and application ports, etc.) for highly flexible and detailed resource utilization accounting. Service providers may utilize the information for billing based on time-of-day, bandwidth usage, application usage, quality of service, etc. Enterprise customers may utilize the information for departmental charge-back or cost allocation for resource utilization.
NetFlow Data Warehousing and Data Mining—NetFlow data (or derived information) can be warehoused for later retrieval and analysis in support of proactive marketing and customerservice programs (e.g. figure out which applications and services are being utilized by internal and external users and target them for improved service, advertising, etc.). In addition, NetFlow data gives Market Researchers access to the "who", "what", "where", and "how long" information relevant to enterprises and service providers.
NEW QUESTION 3
A router receives information about network 192.168.10.0/24 from multiple sources. What will the router consider the most reliable information about the path to that network?
- A. an OSPF update for network 192.168.0.0/16
- B. a static route to network 192.168.10.0/24
- C. a static route to network 192.168.10.0/24 with a local serial interface configured as the next hop
- D. a RIP update for network 192.168.10.0/24
- E. a directly connected interface with an address of 192.168.10.254/24
- F. a default route with a next hop address of 192.168.10.1
Answer: E
Explanation: What Is Administrative Distance? http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk365/technologies_tech_note09186a0080094195.shtml
Select the Best Path
Administrative distance is the first criterion that a router uses to determine which routing protocol to use if two protocols provide route information for the same destination. Administrative distance is a measure of the trustworthiness of the source of the routing information. Administrative distance has only local significance, and is not advertised in
routing updates.
Note: The smaller the administrative distance value, the more reliable the protocol. For example, if a router receives a route to a certain network from both Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) (default administrative distance - 110) and Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (IGRP) (defaultadministrative distance - 100), the router chooses IGRP because IGRP is more reliable. This means the router adds the IGRP version of the route to the routing table.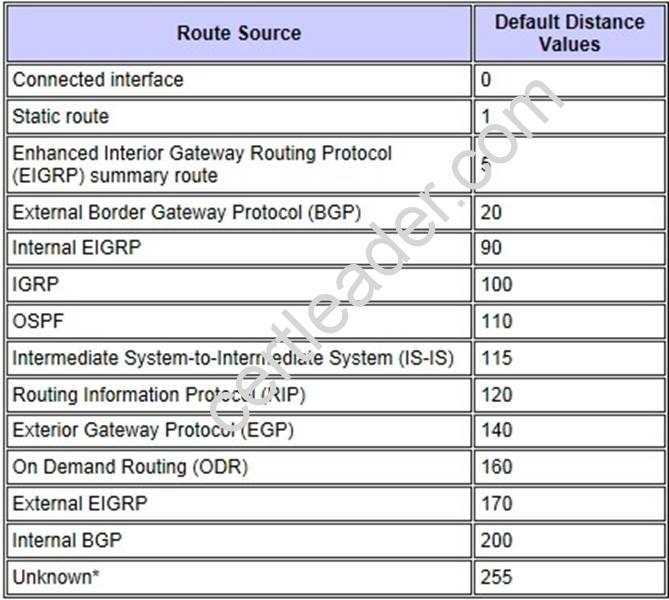
NEW QUESTION 4
DRAG DROP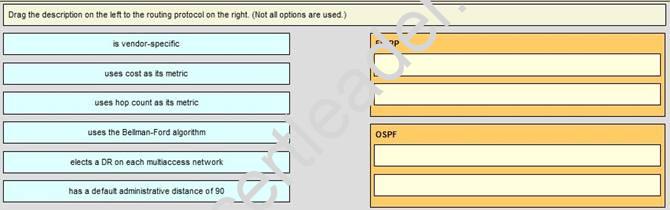
Answer:
Explanation: Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) is a Cisco proprietary routing protocol, so it is vendor-specific. By default, EIGRP internal routes have an administrative distance value of 90.
OSPF uses cost as its metric. By default, the cost of an interface is calculated based on bandwidth with the formula cost= 10000 0000/bandwidth (in bps). OSPF elects a DR on each broadcast and nonbroadcast multiaccess networks (like Ethernet and Frame Relay environments, respectively). It doesn’t elect a DR on point-to-point link (like a serial WAN).
NEW QUESTION 5
Refer to Exhibit:
The internetwork infrastructure of company XYZ consists of a single OSPF area as shown in the graphic. There is concern that a lack of router resources is impeding internetwork performance. As part of examining the router resources, the OSPF DRs need to be known. All the router OSPF priorities are at the default and the router IDs are shown with each router. Which routers are likely to have been elected as DR? (Choose two.)
- A. Corp-1
- B. Corp-2
- C. Corp-3
- D. Corp-4
- E. Branch-1
- F. Branch-2
Answer: DF
Explanation: There are 2 segments on the topology above which are separated by Corp-3 router. Each segment will have a DR so we have 2 DRs.
To select which router will become DR they will compare their router-IDs. The router with highest (best) router-ID will become DR. The router-ID is chosen in the order below:
The highest IP address assigned to a loopback (logical) interface.
If a loopback interface is not defined, the highest IP address of all active router’s physical interfaces will be chosen.
In this question, the IP addresses of loopback interfaces are not mentioned so we will consider IP addresses of all active router’s physical interfaces. Router Corp-4 (10.1.40.40)
& Branch-2 (10.2.20.20) have highest “active” IP addresses so they will become DRs.
NEW QUESTION 6
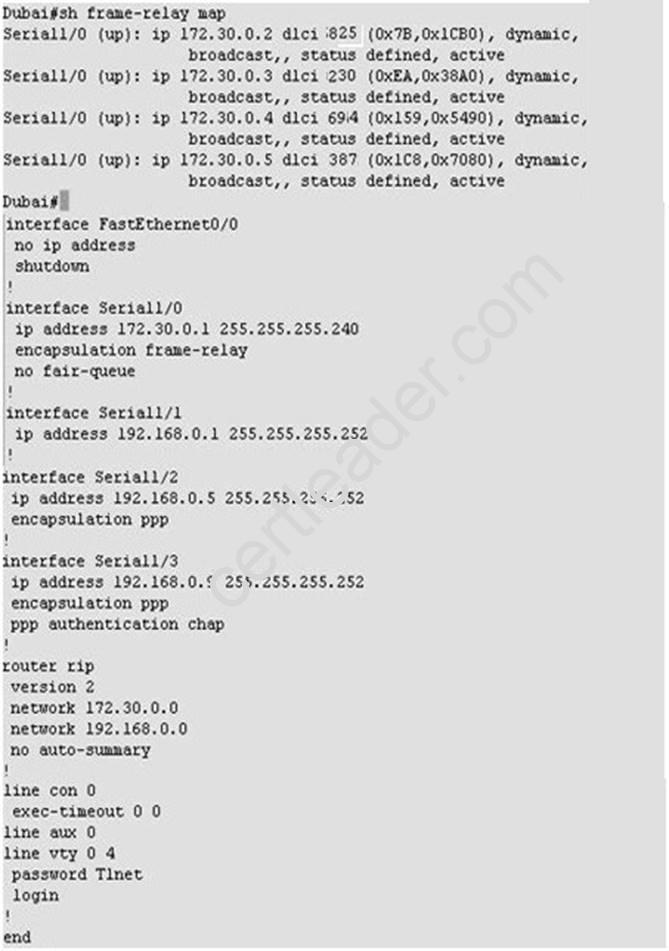
What command is used to verify the DLCI destination address in a Frame Relay static configuration?
- A. show frame-relay pvc
- B. show frame-relay lmi
- C. show frame-relay map
- D. show frame relay end-to-end
Answer: C
Explanation: Cisco Frame Relay Configurations
http://www.ciscopress.com/articles/article.asp?p=170741&seqNum=9 show frame-relay map
The show frame-relay map privileged EXEC mode command shows the contents of the next hop protocol address to DLCI mapping table on the router. The table contains both dynamic mapped and static mapped entries. The below example shows a sample output of the show frame-relay map command.
Router#show frame-relay map
Serial1/2 (up): ip 172.16.1.4 dlci 401(0x191,0x6410), dynamic, broadcast,, status defined, active
Serial1/2 (up): ip 172.16.1.5 dlci 501(0x1F5,0x7C50), dynamic, broadcast,, status defined, active
Serial1/2 (up): ip 172.16.1.2 dlci 301(0x12D,0x48D0), dynamic, broadcast,, status defined, active
NEW QUESTION 7
Refer to the exhibit.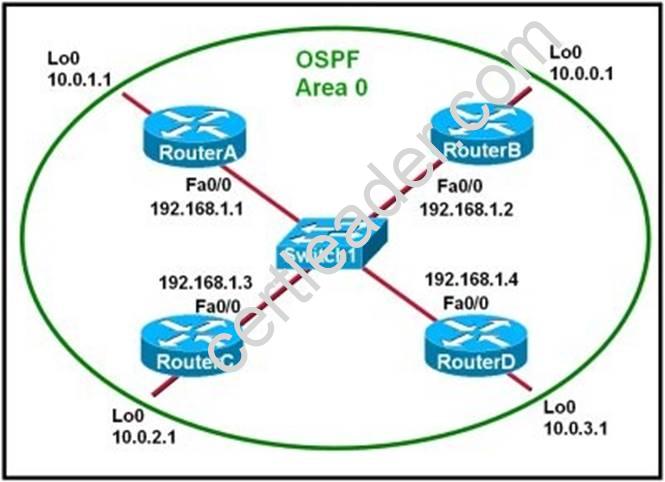
Which two statements are true about the loopback address that is configured on RouterB? (Choose two.)
- A. It ensures that data will be forwarded by RouterB.
- B. It provides stability for the OSPF process on RouterB.
- C. It specifies that the router ID for RouterB should be 10.0.0.1.
- D. It decreases the metric for routes that are advertised from RouterB.
- E. It indicates that RouterB should be elected the DR for the LAN.
Answer: BC
Explanation: A loopback interface never comes down even if the link is broken so it provides stability for the OSPF process (for example we use that loopback interface as the router-id) - B is correct.
The router-ID is chosen in the order below:
The highest IP address assigned to a loopback (logical) interface.If a loopback interface is not defined, the highest IP address of all active router’s physical interfaces will be chosen.
-The loopback interface will be chosen as the router ID of RouterB - C is correct.
NEW QUESTION 8
Refer to the exhibit.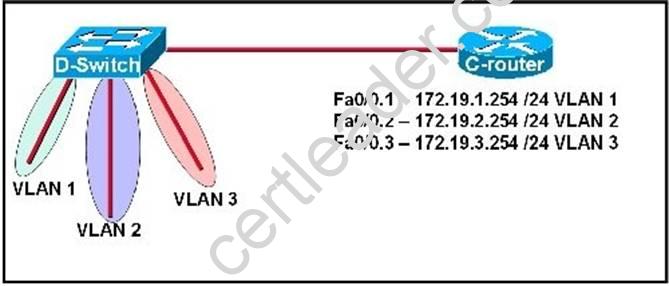
C-router is to be used as a "router-on-a-stick" to route between the VLANs. All the interfaces have been properly configured and IP routing is operational. The hosts in the VLANs have been configured with the appropriate default gateway. What is true about this configuration?
- A. These commands need to be added to the configuration: C-router(config)# router eigrp 123C-router(config-router)# network 172.19.0.0
- B. These commands need to be added to the configuration: C-router(config)# router ospf 1C-router(config-router)# network 172.19.0.0 0.0.3.255 area 0
- C. These commands need to be added to the configuration: C-router(config)# router ripC-router(config-router)# network 172.19.0.0
- D. No further routing configuration is required.
Answer: D
Explanation: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk389/tk815/technologies_configuration_example09186a 00800949fd.shtml
https://learningnetwork.cisco.com/servlet/JiveServlet/download/5669-2461/Router%20on%20a%20Stick.pdf.
NEW QUESTION 9
What are three reasons to collect Netflow data on a company network? (Choose three.)
- A. To identify applications causing congestion
- B. To authorize user network access
- C. To report and alert link up / down instances
- D. To diagnose slow network performance, bandwidth hogs, and bandwidth utilization
- E. To detect suboptimal routing in the network
- F. To confirm the appropriate amount of bandwidth that has been allocated to each Class of Service
Answer: ADF
NEW QUESTION 10
Refer to the exhibit.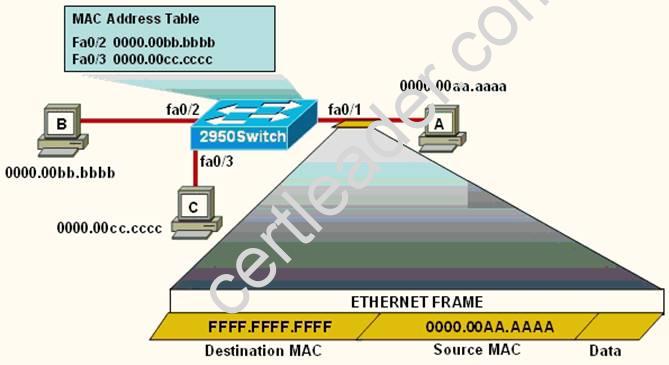
The following commands are executed on interface fa0/1 of 2950Switch.
2950Switch(config-if)# switchport port-security
2950Switch(config-if)# switchport port-security mac-address sticky
2950Switch(config-if)# switchport port-security maximum 1
The Ethernet frame that is shown arrives on interface fa0/1. What two functions will occur when this frame is received by 2950Switch? (Choose two.)
- A. The MAC address table will now have an additional entry of fa0/1 FFFF.FFFF.FFFF.
- B. Only host A will be allowed to transmit frames on fa0/1.
- C. This frame will be discarded when it is received by 2950Switch.
- D. All frames arriving on 2950Switch with a destination of 0000.00aa.aaaa will be forwarded out fa0/1.
- E. Hosts B and C may forward frames out fa0/1 but frames arriving from other switches will not be forwarded out fa0/1.
- F. Only frames from source 0000.00bb.bbbb, the first learned MAC address of 2950Switch, will be forwarded out fa0/1.
Answer: BD
NEW QUESTION 11
Which three statements about RSTP are true? (Choose three.)
- A. RSTP significantly reduces topology reconverging time after a link failure.
- B. RSTP expands the STP port roles by adding the alternate and backup roles.
- C. RSTP port states are blocking, discarding, learning, or forwarding.
- D. RSTP provides a faster transition to the forwarding state on point-to-point links than STP does.
- E. RSTP also uses the STP proposal-agreement sequence.
- F. RSTP uses the same timer-based process as STP on point-to-point links.
Answer: ABD
Explanation: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk389/tk621/technologies_white_paper09186a0080094cf a.shtml
Convergence
Cisco enhanced the original 802.1D specification with features such as Uplink Fast, Backbone Fast, and Port Fast to speed up the convergence time of a bridged network. The drawback is that these mechanisms are proprietary and need additional configuration.
Alternate and Backup Port Roles
These two port roles correspond to the blocking state of 802.1D. A blocked port is defined as not being the designated or root port. A blocked port receives a more useful BPDU than the one it sends out on its segment.
Remember that a port absolutely needs to receive BPDUs in order to stay blocked. RSTP introduces these two roles for this purpose.
Rapid Transition to Forwarding State
Rapid transition is the most important feature introduced by 802.1w. The legacy STA passively waited for the network to converge before it turned a port into the forwarding state. The achievement of faster convergence was a matter of tuning the conservative default parameters (forward delay and max_age timers) and often put the stability of the network at stake. The new rapid STP is able to actively confirm that a port can safely
transition to the forwarding state without having to rely on any timer configuration. There is now a real feedback mechanism that takes place between RSTP-compliant bridges. In order to achieve fast convergence on a port, the protocol relies upon two new variables: edge ports and link type.
Topic 2, IP Routing Technologies
NEW QUESTION 12
What are three values that must be the same within a sequence of packets for Netflow to consider them a network flow? (Choose three.)
- A. source IP address
- B. source MAC address
- C. egress interface
- D. ingress interface
- E. destination IP address
- F. IP next-hop
Answer: ADE
NEW QUESTION 13
Refer to the exhibit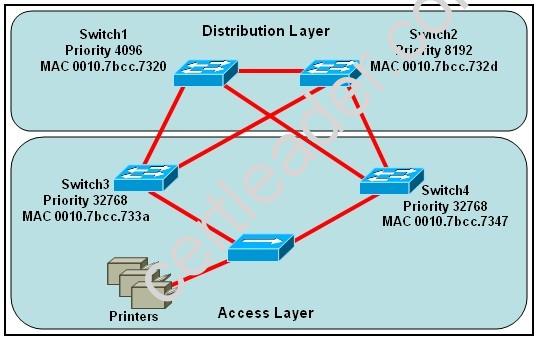
Which switch provides the spanning-tree designated port role for the network segment that services the printers?
- A. Switch1
- B. Switch2
- C. Switch3
- D. Switch4
Answer: C
Explanation: First, the question asks what switch services the printers, so it can be Switch 3 or Switch 4 which is connected directly to the Printers.
Designated port is a port that is in the forwarding state. All ports of the root bridge are designated ports.
Switch 3 and Switch 4 has same priority so it will see on lowest MAC address and here switch 3 has lowest MAC address. So switch 3 segment will play a Designated port role. By comparing the MAC address of Switch 3 and Switch 4 we found that the MAC of Switch 3 is smaller. Therefore the interface connected to the Printers of Switch 3 will become designated interface and the interface of Switch 4 will be blocked.
NEW QUESTION 14
Which protocol provides a method of sharing VLAN configuration information between two Cisco switches?
- A. STP
- B. VTP
- C. 802.1Q
- D. RSTP
Answer: B
Explanation: Understanding VLAN Trunk Protocol (VTP) http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk389/tk689/technologies_tech_note09186a0080094c52. shtml
Introduction
VLAN Trunk Protocol (VTP) reduces administration in a switched network. When you configure a new VLAN on one VTP server, the VLAN is distributed through all switches in the domain. This reduces the need to configure the same VLAN everywhere. VTP is a Cisco-proprietary protocol that is available on most of the Cisco Catalyst series products.
NEW QUESTION 15
Which term describes a spanning-tree network that has all switch ports in either the blocking or fowarding state?
- A. converged
- B. redundant
- C. provisioned
- D. spanned
Answer: A
Explanation: Spanning Tree Protocol convergence (Layer 2 convergence) happens when bridges and switches have transitioned to either the forwarding or blocking state. When layer 2 is converged, root bridge is elected and all port roles (Root, Designated and Non-Designated) in all switches are selected.
NEW QUESTION 16
The following configuration is applied to a Layer 2 Switch:
interface fastethernet 0/4
switchport mode access
switchport port-security
switchport port-security mac-address 0000.1111.1111
switchport port-security maximum 2
swithcport port-security
What is the result of the above configuration being applied to the switch?
- A. A host with a mac address of 0000.1111.1111 and up to two other hosts can connect to FastEthernet 0/4 simultaneously
- B. A host with a mac address of 0000.1111.1111 and one other host can connect to Fast Ethernet 0/4 simultaneously
- C. Violating addresses are dropped and no record of the violation is kept
- D. The switch can send an SNMP message to the network management station
- E. The port is effectively shutdown
Answer: BD
Explanation: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/switches/lan/catalyst4500/12.2/20ewa/configuration/guid e/port_sec.html
NEW QUESTION 17
A network administrator needs to configure port security on a switch. Which two statements are true? (Choose two.)
- A. The network administrator can apply port security to dynamic access ports.
- B. When dynamic MAC address learning is enabled on an interface, the switch can learn new addresses, up to the maximum defined.
- C. The sticky learning feature allows the addition of dynamically learned addresses to the running configuration.
- D. The network administrator can configure static secure or sticky secure MAC addresses in the voice VLAN.
- E. The network administrator can apply port security to EtherChannels.
Answer: BC
NEW QUESTION 18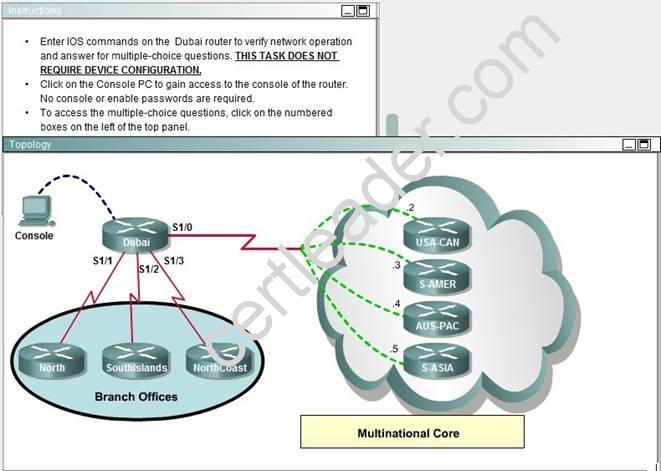
Which connection uses the default encapsulation for serial interfaces on Cisco routers?
- A. The serial connection to the NorthCoast branch office.
- B. The serial connection to the North branch office.
- C. The serial connection to the Southlands branch office.
- D. The serial connection to the Multinational Core.
Answer: B
Explanation: Cisco default encapsulation is HDLC which is by default enabled on all cisco router. If we want to enable other encapsulation protocol(PPP,X.25 etc) we need to define in interface setting. But here except s1/1 all interface defined by other encapsulation protocol so we will assume default encapsulation running on s1/1 interface and s1/1 interface connected with North
NEW QUESTION 19
What are three characteristics of the OSPF routing protocol? (Choose three.)
- A. It converges quickly.
- B. OSPF is a classful routing protocol.
- C. It uses cost to determine the best route.
- D. It uses the DUAL algorithm to determine the best route.
- E. OSPF routers send the complete routing table to all directly attached routers.
- F. OSPF routers discover neighbors before exchanging routing information.
Answer: ACF
Explanation: Open Shortest Path First Reference:
http://docwiki.cisco.com/wiki/Open_Shortest_Path_First
Additional OSPF features include equal-cost, multipath routing, and routing based on upper-layer type-ofservice
(TOS) requests. TOS-based routing supports those upper-layer protocols that can specify particular
types of service. An application, for example, might specify that certain data is urgent. If OSPF has high-priority
links at its disposal, these can be used to transport the urgent datagram.
OSPF supports one or more metrics. If only one metric is used, it is considered to be arbitrary, and TOS is not supported. If more than one metric is used, TOS is optionally supported through the use of a separate metric (and, therefore, a separate routing table) for each of the eight combinations created by the three IP TOS bits (the delay, throughput, and reliability bits). For example, if the IP TOS bits specify low delay, low throughput, and high reliability, OSPF calculates routes to all destinations based on this TOS designation. IP subnet masks are included with each advertised destination, enabling variable-length subnet masks. With variable-length subnet masks, an IP network can be broken into many subnets of various sizes. This provides network administrators with extra network- configuration flexibility.
Topic 3, IP Services
P.S. Easily pass 200-101 Exam with 149 Q&As Certshared Dumps & pdf Version, Welcome to Download the Newest Certshared 200-101 Dumps: https://www.certshared.com/exam/200-101/ (149 New Questions)