Our pass rate is high to 98.9% and the similarity percentage between our and real exam is 90% based on our seven-year educating experience. Do you want achievements in the Cisco 200-101 exam in just one try? I am currently studying for the . Latest , Try Cisco 200-101 Brain Dumps First.
Online 200-101 free questions and answers of New Version:
NEW QUESTION 1
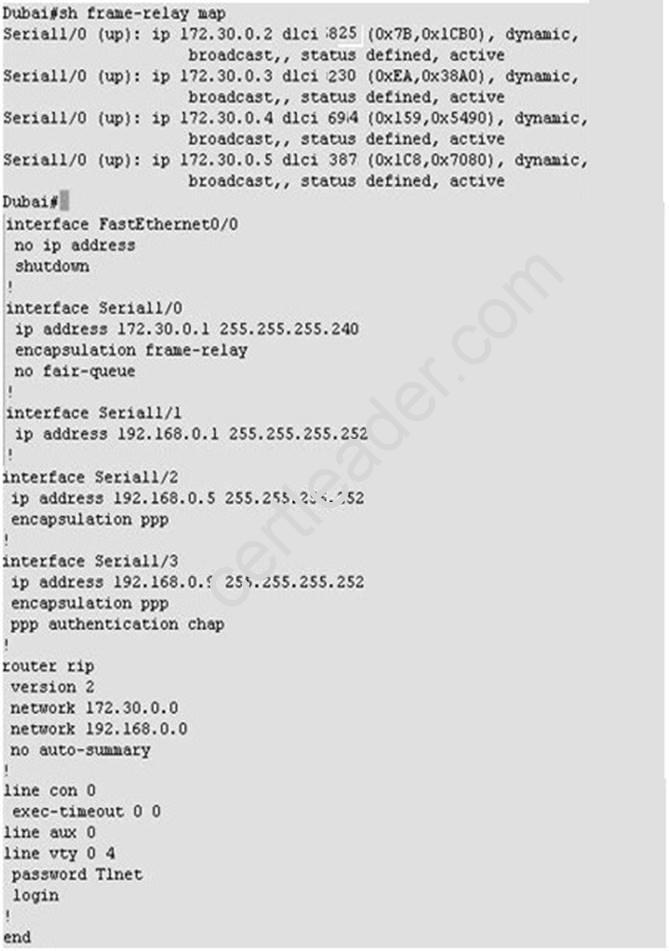
What would be the destination Layer 2 address in the frame header for a frame that is being forwarded by Dubai to the host address of 172.30.4.4?
- A. 825
- B. 230
- C. 694
- D. 387
Answer: C
Explanation: According to command output 172.30.4.4 is using the 694 dlci value. http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/12_2/wan/command/reference/wrffr4.html#wp102934 3
NEW QUESTION 2
Which encapsulation type is a Frame Relay encapsulation type that is supported by Cisco routers?
- A. IETF
- B. ANSI Annex D
- C. Q9333-A Annex A
- D. HDLC
Answer: A
Explanation: Cisco supports two Frame Relay encapsulation types: theCisco encapsulationand the IETF Frame Relay encapsulation, which is in conformance with RFC 1490 and RFC 2427. The former is often used to connect two Cisco routers while the latter is used to connect a Cisco router to a non-Cisco router. You can test with your Cisco router when typing the command Router(config-if)#encapsulation frame-relay ?on a WAN link.
Note: Three LMI options are supported by Cisco routers are ansi, Cisco, and Q933a. They represent the ANSI Annex D, Cisco, and ITU Q933-A (Annex A) LMI types, respectively. HDLC is a WAN protocol same as Frame-Relay and PPP so it is not a Frame Relay encapsulation type.
NEW QUESTION 3
Refer to the exhibit.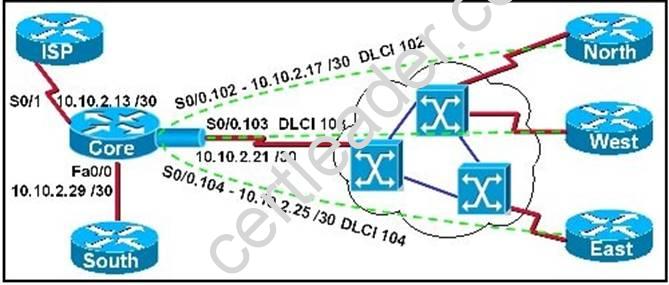
The network associate is configuring OSPF on the Core router. All the connections to the branches should be participating in OSPF. The link to the ISP should NOT participate in OSPF and should only be advertised as the default route. What set of commands will properly configure the Core router?
- A. Core(config-router)# default-information originate Core(config-router)# network 10.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 0 Core(config-router)# exitCore(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.10.2.14
- B. Core(config-router)# default-information originate Core(config-router)# network 10.10.2.13 0.0.0.242 area 0 Core(config-router)# exitCore(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.10.2.14
- C. Core(config-router)# default-information originate Core(config-router)# network 10.10.2.16 0.0.0.15 area 0 Core(config-router)# exitCore(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.10.2.14
- D. Core(config-router)# default-information originate Core(config-router)# network 10.10.2.32 0.0.0.31 area 0 Core(config-router)# exitCore(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.10.2.14
Answer: C
Explanation: There are two ways to inject a default route into a normal area.1. If the ASBR already has the default route in its routing table, you can advertise theexisting 0.0.0.0/0 into the OSPF domain with the default-information originate router configuration command.2. If the ASBR doesn’t have a default route, you can add the keyword always to the default- information originate command (default-information originate always).This command will advertise a default route into the OSPF domain, regardless of whether it has a route to
0.0.0.0. Another benefit of adding always keyword is that it can add stability to the internetwork. For example, if the ASBR is learning a default route from another routing domain such as RIP and this route is flapping, then without the always keyword, each time the route flaps, the ASBR will send a new Type 5 LSA into the OSPF domain causing some instability inside the OSPF domain. With the always keyword, the ASBR will advertise the default inside the OSPF domain always,In the example shown here, only choice C is correct as the wildcard mask correctly specifies the 10.10.2.16 0.0.0.15 networks, which include all IP addresses in the 10.10.2.16-10.10.2.31 range. In this question we were told that the ISP link should NOT be configured for OSPF, making choice A incorrect. http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk365/technologies_configuration_example09186a00801 ec9f0.shtml
NEW QUESTION 4
Refer to the exhibit.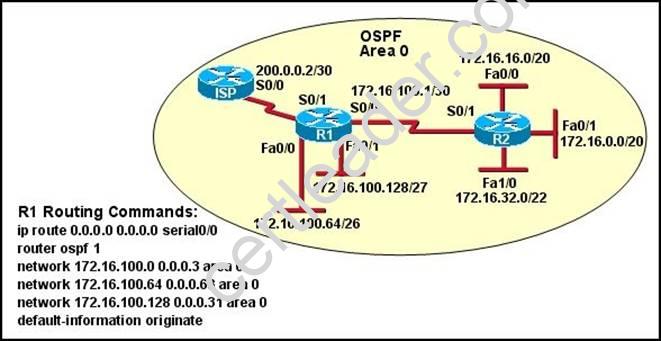
Assume that all router interfaces are operational and correctly configured. In addition, assume that OSPF has been correctly configured on router R2. How will the default route configured on R1 affect the operation of R2?
- A. Any packet destined for a network that is not directly connected to router R1 will be dropped.
- B. Any packet destined for a network that is not directly connected to router R2 will be dropped immediately.
- C. Any packet destined for a network that is not directly connected to router R2 will be dropped immediately because of the lack of a gateway on R1.
- D. The networks directly connected to router R2 will not be able to communicate with the 172.16.100.0, 172.16.100.128, and 172.16.100.64 subnetworks.
- E. Any packet destined for a network that is not referenced in the routing table of router R2 will be directed to R1. R1 will then send that packet back to R2 and a routing loop will occur.
Answer: E
Explanation: First, notice that the more-specific routes will always be favored over less-specific routes regardless of the administrative distance set for a protocol. In this case, because we use OSPF for three networks (172.16.100.0 0.0.0.3, 172.16.100.64 0.0.0.63, 172.16.100.128
0.0.0.31) so the packets destined for these networks will not be affected by the default route. The default route configured on R1 "ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 serial0/0 will send any packet whose destination network is not referenced in the routing table of router R1 to R2, it doesn't drop anything so answers A, B and C are not correct. D is not correct too because these routes are declared in R1and the question says that "OSPF has been correctly configured on router R2, so network directly connected to router R2 can communicate with those three subnetworks. As said above, the default route configured on R1 will send any packet destined for a network that is not referenced in its routing table to R2; R2 in turn sends it to R1 because it is the only way and a routing loop will occur.
NEW QUESTION 5
Refer to the exhibit.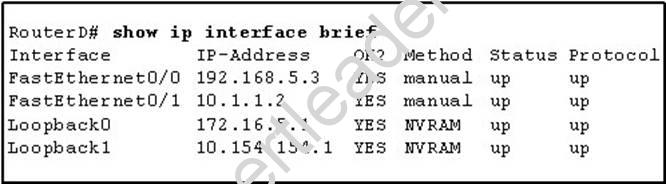
Given the output for this command, if the router ID has not been manually set, what router ID will OSPF use for this router?
- A. 10.1.1.2
- B. 10.154.154.1
- C. 172.16.5.1
- D. 192.168.5.3
Answer: C
Explanation: CCNA Tutorial: The OSPF Router ID (RID) http://www.thebryantadvantage.com/CCNACertificationExamTutorialOSPFRouterIDRID.ht m
When determining the Router ID (RID) of an OSPF-enabled router, OSPF will always use the numerically highest IP address on the router’s loopback interfaces, regardless of whether that loopback is OSPF-enabled.
What if there is no loopback? OSPF will then use the numerically highest IP address of the physical interfaces, regardless of whether that interface is OSPF-enabled.
NEW QUESTION 6
DRAG DROP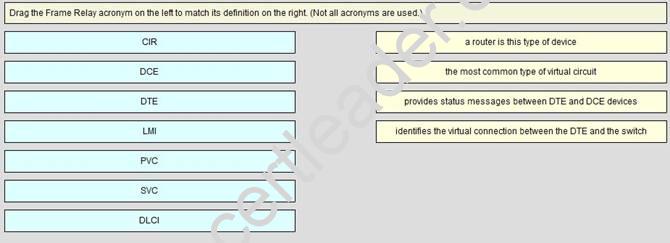
Answer:
Explanation: 1) a router is this type of device: DTE2) the most common type of virtual circuit: PVC3) provides status messages between DTE and DCE devices: LMI4) identifies the virtual connection between the DTE and the switch: DLCI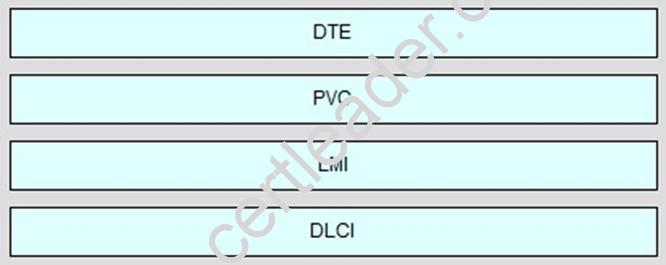
CCNA Certification Test Prep Case Study http://www.thebryantadvantage.com/CCNACertificationExamTutorialDirectlyConnectedSerialInterfaces.htm
Configuring the LMI Type on a Frame Relay Interface http://www.ciscopress.com/articles/article.asp?p=170741&seqNum=3
Frame Relay DLCIs And Mappings
http://www.mcmcse.com/cisco/guides/frame_relay_dlci.shtml
NEW QUESTION 7
Scenario
Refer to the topology. Your company has connected the routers R1. R2. and R3 with serial links. R2 and R3 are connected to the switches SW1 and SW2, respectively. SW1 and SW2 are also connected to the routers R4 and R5.
The EIGRP routing protocol is configured.
You are required to troubleshoot and resolve the EIGRP issues between the various routers.
Use the appropriate show commands to troubleshoot the issues.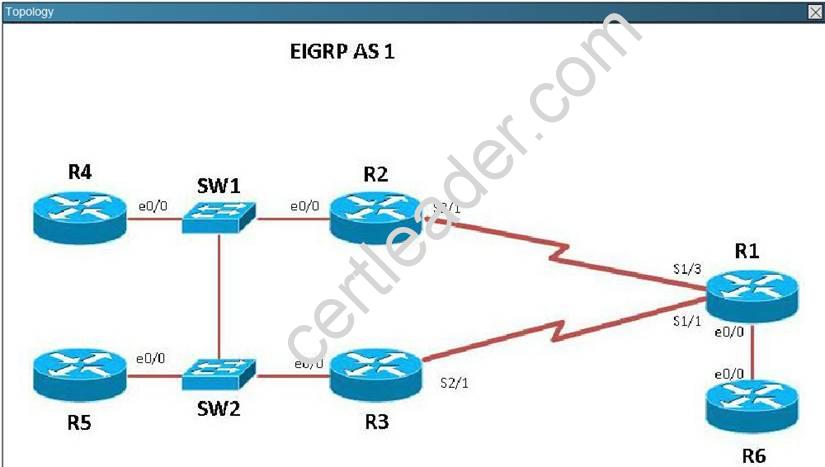

The loopback interfaces on R4 with the IP addresses of 10.4.4.4 /32, 10.4.4.5/32. and 10.4.4.6/32 are not appearing in the routing table of R5 Why are the interfaces missing?
- A. The interfaces are shutdown, so they are not being advertised.
- B. R4 has been incorrectly configured to be in another AS, so it does not peer with R5.
- C. Automatic summarization is enabled, so only the 10.0.0.0 network is displayed.
- D. The loopback addresses haven't been advertised, and the network command is missing on R4.
Answer: B
Explanation: For an EIGRP neighbor to form, the following must match:
- Neighbors must be in the same subnet- K values- AS numbers- Authentication method and key strings
Here, we see that R4 is configured for EIGRP AS 2, when it should be AS 1.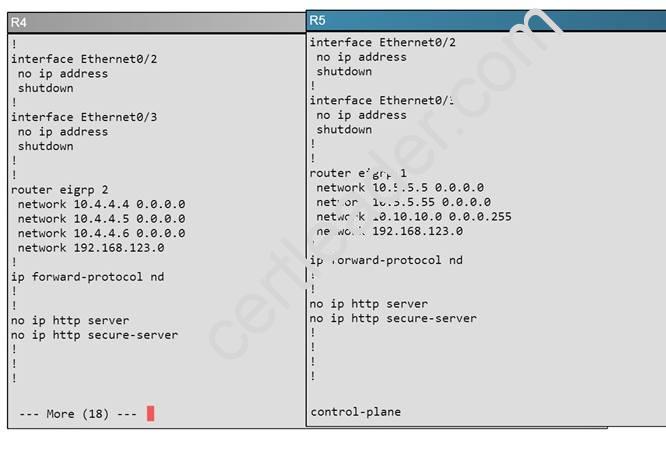
NEW QUESTION 8
The command show frame-relay map gives the following output:
Serial 0 (up): ip 192.168.151.4 dlci 122, dynamic, broadcast, status defined, active Which statements represent what is shown?(Choose three.)
- A. 192.168.151.4 represents the IP address of the remote router
- B. 192.168.151.4 represents the IP address of the local serial interface
- C. DLCI 122 represents the interface of the remote serial interface
- D. DLCI 122 represents the local number used to connect to the remote address
- E. broadcast indicates that a dynamic routing protocol such as RIP v1 can send packets across this PVC
- F. active indicates that the ARP process is working
Answer: ADE
Explanation: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/12_2/wan/command/reference/wrffr4.html#wp102934 3
NEW QUESTION 9
What are two characteristics of Frame Relay point-to-point subinterfaces? (Choose two.)
- A. They create split-horizon issues.
- B. They require a unique subnet within a routing domain.
- C. They emulate leased lines.
- D. They are ideal for full-mesh topologies.
- E. They require the use of NBMA options when using OSPF.
Answer: BC
Explanation: http://www.ciscopress.com/articles/article.asp?p=170741&seqNum=5
Configuring Frame Relay Subinterfaces
On partially meshed Frame Relay networks, the problem of split horizon can be overcome by using Frame Relay subinterfaces. Frame Relay provides a mechanism to allow a physical interface to be partitioned into multiple virtual interfaces. In a similar way, using subinterfaces allows a partially meshed network to be divided into a number of smaller, fully meshed point-to-point networks. Generally, each point-to-point subnetwork is assigned a unique network address. This allows packets received on one physical interface to be sent out from the same physical interface, albeit forwarded on VCs in different subinterfaces.
There are two types of subinterfaces supported by Cisco routers: point-to-point and multipoint subinterfaces.
NEW QUESTION 10
Refer to the exhibit.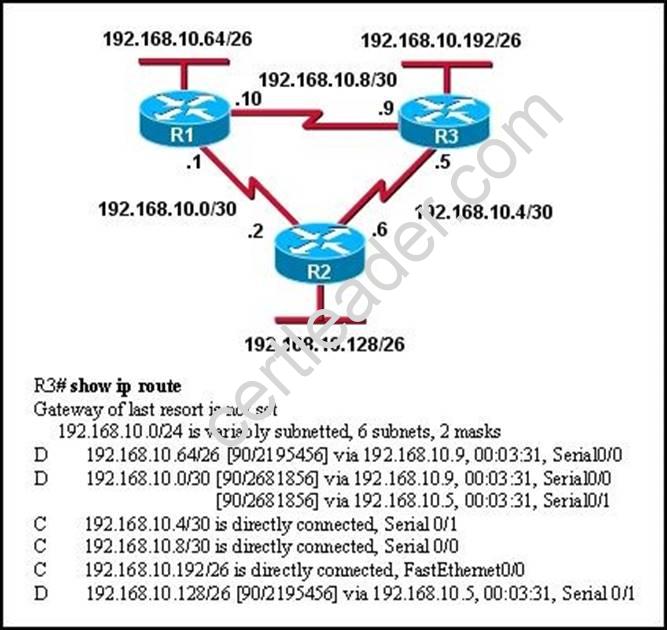
Based on the exhibited routing table, how will packets from a host within the 192.168.10.192/26 LAN be forwarded to 192.168.10.1?
- A. The router will forward packets from R3 to R2 to R1.
- B. The router will forward packets from R3 to R1 to R2.
- C. The router will forward packets from R3 to R2 to R1 AND from R3 to R1.
- D. The router will forward packets from R3 to R1.
Answer: C
Explanation: From the routing table we learn that network 192.168.10.0/30 is learned via 2 equal- cost paths (192.168.10.9 &192.168.10.5) - traffic to this network will be load-balanced.
NEW QUESTION 11
Which two statements describe the process identifier that is used in the command to configure OSPF on a router? (Choose two.)
Router(config)# router ospf 1
- A. All OSPF routers in an area must have the same process ID.
- B. Only one process number can be used on the same router.
- C. Different process identifiers can be used to run multiple OSPF processes
- D. The process number can be any number from 1 to 65,535.
- E. Hello packets are sent to each neighbor to determine the processor identifier.
Answer: CD
Explanation: we all know that The areas can be any number from 0 to 4.2 billion and 1 to 65,535 for the Process ID.
The process ID is the ID of the OSPF process to which the interface belongs. The process ID is local to the router, and two OSPF neighboring routers can have different OSPF process IDs. (This is not true of Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol [EIGRP], in which the routers need to be in the same autonomous system). Cisco IOS Software can run multiple OSPF processes on the same router, and the process ID merely distinguishes one process from the another. The process ID should be a positive integer.
NEW QUESTION 12
Which of these represents an IPv6 link-local address?
- A. FE80::380e:611a:e14f:3d69
- B. FE81::280f:512b:e14f:3d69
- C. FEFE:0345:5f1b::e14d:3d69
- D. FE08::280e:611:a:f14f:3d69
Answer: A
Explanation: Understanding IPv6 Link Local Address Reference:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk872/technologies_configuration_example09186a0080b a1d07.shtml
The purpose of this document is to provide an understanding of IPv6 Link-local address in a network. A linklocal address is an IPv6 unicast address that can be automatically configured on any interface using the linklocal prefix FE80::/10 (1111 1110 10) and the interface identifier in the modified EUI-64 format. Link-local addresses are not necessarily bound to the MAC address (configured in a EUI-64 format). Link-local addresses can also be manually configured in the FE80::/10 format using the ipv6 address link-local command.
NEW QUESTION 13
Refer to the exhibit.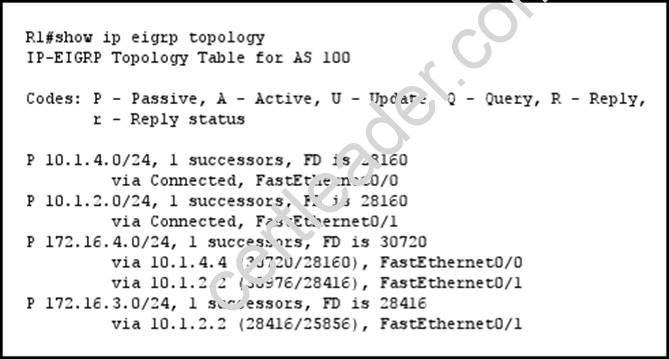
What address is a feasible successor?
- A. 172.16.4.0
- B. 10.1.4.4
- C. 10.1.2.2
- D. 172.16.3.0
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 14
A router is running three routing processes: RIP, OSPF, and EIGRP, each configured with default characteristics. Each process learns a route to the same remote network.
If there are no static routes to the destination and none of the routes were redistributed, which route will be placed in the IP routing table?
- A. the route learned through EIGRP
- B. the route learned through OSPF
- C. the route learned through RIP
- D. the route with the lowest metric
- E. all three routes with the router load balancing
Answer: A
Explanation: Reference: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk365/technologies_tech_note09186a0080094195.shtml
Administrative distance is the feature that routers use in order to select the best path. Administrative distance defines the reliability of a routing protocol. Each routing protocol is prioritized in order of most to least reliable (believable) with the help of an administrative distance value. Lowest Administrative distance will be chosen first.
NEW QUESTION 15
- A. RSTP cannot operate with PVST+.
- B. RSTP defines new port roles.
- C. RSTP defines no new port states.
- D. RSTP is a proprietary implementation of IEEE 802.1D STP.
- E. RSTP is compatible with the original IEEE 802.1D STP.
Answer: BE
Explanation: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk389/tk621/technologies_white_paper09186a0080094cf a.shtml
Port Roles
The role is now a variable assigned to a given port. The root port and designated port roles remain, while the blocking port role is split into the backup and alternate port roles. The Spanning Tree Algorithm (STA) determines the role of a port based on Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDUs). In order to simplify matters, the thing to remember about a BPDU is there is always a method to compare any two of them and decide whether one is more useful than the other. This is based on the value stored in the BPDU and occasionally on the port on which they are received. This considered, the information in this section explains practical approaches to port roles.
Compatibility with 802.1D
RSTP is able to interoperate with legacy STP protocols. However, it is important to note that the inherent fast convergence benefits of 802.1w are lost when it interacts with legacy bridges.
NEW QUESTION 16
It has become necessary to configure an existing serial interface to accept a second Frame Relay virtual circuit. Which of the following are required to solve this? (Choose three)
- A. configure static frame relay map entries for each subinterface network.
- B. remove the ip address from the physical interface
- C. create the virtual interfaces with the interface command
- D. configure each subinterface with its own IP address
- E. disable split horizon to prevent routing loops between the subinterface networks
- F. encapsulate the physical interface with multipoint PPP
Answer: BCD
Explanation: How To Configure Frame Relay Subinterfaces
http://www.orbit-computer-solutions.com/How-To-Configure-Frame-Relay- Subinterfaces.php
Step to configure Frame Relay subinterfaces on a physical interface:
1. Remove any network layer address (IP) assigned to the physical interface. If the physical interface has an address, frames are not received by the local subinterfaces.
2. Configure Frame Relay encapsulation on the physical interface using the encapsulation frame-relay command.
3. For each of the defined PVCs, create a logical subinterface. Specify the port number, followed by a period (.) and the subinterface number. To make troubleshooting easier, it is suggested that the subinterface number matches the DLCI number.
4. Configure an IP address for the interface and set the bandwidth.
5. Configure the local DLCI on the subinterface using the frame-relay interface-dlci command.
Configuration Example: R1>enable R1#configure terminal
R1(config)#interface serial 0/0/0 R1(config-if)#no ip address
R1(config-if)#encapsulation frame-relay R1(config-if)#no shutdown
R1(config-if)#exit
R1(config-subif)#interface serial 0/0/0.102 point-to-point
R1(config-subif)#ip address 192.168.1.245 255.255.255.252
R1(config-subif)#frame-relay interface-dlci 102 R1(config-subif)#end
R1#copy running-config startup-config
NEW QUESTION 17
Refer to the exhibit.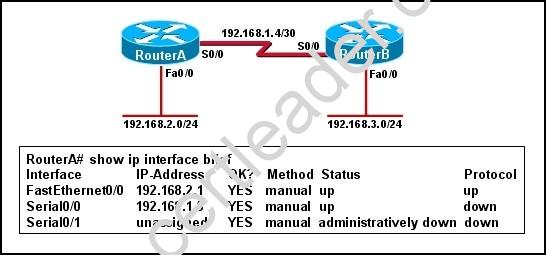
Hosts in network 192.168.2.0 are unable to reach hosts in network 192.168.3.0. Based on the output from RouterA, what are two possible reasons for the failure? (Choose two.)
- A. The cable that is connected to S0/0 on RouterA is faulty.
- B. Interface S0/0 on RouterB is administratively down.
- C. Interface S0/0 on RouterA is configured with an incorrect subnet mask.
- D. The IP address that is configured on S0/0 of RouterB is not in the correct subnet.
- E. Interface S0/0 on RouterA is not receiving a clock signal from the CSU/DSU.
- F. The encapsulation that is configured on S0/0 of RouterB does not match the encapsulation that is configured on S0/0 of RouterA.
Answer: EF
Explanation: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/routers/access/800/819/software/configuration/Guide/6se r_conf.html
NEW QUESTION 18
Which two statements about using the CHAP authentication mechanism in a PPP link are true? (Choose two.)
- A. CHAP uses a two-way handshake.
- B. CHAP uses a three-way handshake.
- C. CHAP authentication periodically occurs after link establishment.
- D. CHAP authentication passwords are sent in plaintext.
- E. CHAP authentication is performed only upon link establishment.
- F. CHAP has no protection from playback attacks.
Answer: BC
Explanation: Understanding and Configuring PPP CHAP Authentication http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk713/tk507/technologies_tech_note09186a00800b4131. shtml
One-Way and Two-Way Authentication
CHAP is defined as a one-way authentication method. However, you use CHAP in both directions to create a two-way authentication. Hence, with two-way CHAP, a separate three-way handshake is initiated by each side. In the Cisco CHAP implementation, by
default, the called party must authenticate the calling party (unless authentication is completely turned off). Therefore, a one-way authentication initiated by the called party is the minimum possible authentication. However, the calling party can also verify the identity of the called party, and this results in a two-way authentication.
One-way authentication is often required when you connect to non-Cisco devices.
NEW QUESTION 19
Refer to the exhibit.
A network associate has configured OSPF with the command: City(config-router)# network 192.168.12.64 0.0.0.63 area 0
After completing the configuration, the associate discovers that not all the interfaces are participating in OSPF. Which three of the interfaces shown in the exhibit will participate in OSPF according to this configuration statement? (Choose three.)
- A. FastEthernet0 /0
- B. FastEthernet0 /1
- C. Serial0/0
- D. Serial0/1.102
- E. Serial0/1.103
- F. Serial0/1.104
Answer: BCD
Explanation: The “network 192.168.12.64 0.0.0.63 equals to network 192.168.12.64/26. This network has:Increment: 64 (/26= 1111 1111.1111 1111.1111 1111.1100 0000)Network address:
192.168.12.64
Broadcast address: 192.168.12.127Therefore all interface in the range of this network will join OSPF - B C D are correct.
100% Valid and Newest Version 200-101 Questions & Answers shared by Passcertsure, Get Full Dumps HERE: https://www.passcertsure.com/200-101-test/ (New 149 Q&As)